Effects of Preoperative Glycyrrhizin Infusion for the Prevention of Venous Thrombosis on the Tissue Expression of Antithrombin in a Rat Model
- PMID: 27375802
- PMCID: PMC4919301
- DOI: 10.3400/avd.oa.16-00009
Effects of Preoperative Glycyrrhizin Infusion for the Prevention of Venous Thrombosis on the Tissue Expression of Antithrombin in a Rat Model
Abstract
Objective: Using a thrombus model prepared by ligation of the inferior vena cava (IVC), the influences of the glycoside, glycyrrhizin, on plasma antithrombin levels and antithrombin mRNA expression levels in the liver and IVC with the inhibition of venous thrombosis were investigated.
Materials and methods: The rat IVC was exposed and ligated for 24 h immediately after the intravenous administration of 300 mg/kg glycyrrhizin. Among antithrombotic drugs, the Xa inhibitor, fondaparinux sodium, was used as a control drug.
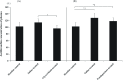
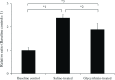
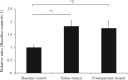
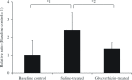
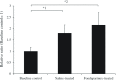
Results: The mean thrombus weight was significantly smaller in the glycyrrhizin-treated group (18.3 mg) than in the saline-treated group (34.3 mg). In contrast, the inhibition of thrombosis was not observed in the fondaparinux-treated group. Antithrombin mRNA expression levels in the liver were significantly higher in the ligated groups than in the baseline control group. The mean plasma antithrombin level was significantly lower in the glycyrrhizin group (96.6%) than in the saline group (114.4%), but was not significantly different from that in the baseline control group (102.4%).
Conclusion: The pretreatment with glycyrrhizin inhibited venous thrombosis, and antithrombin mRNA expression levels in the liver and IVC as well as plasma antithrombin levels were significantly lower than those in the saline group.
Keywords: DVT; antithrombin; glycyrrhizin.
Figures
References
-
- Vinazzer H. Clinical use of antithrombin III concentrates. Vox Sang 1987; 53: 193-8. - PubMed
-
- Griffith MJ. Kinetic analysis of the heparin-enhanced antithrombin III/thrombin reaction. Reaction rate enhancement by heparin-thrombin association. J Biol Chem 1979; 254: 12044-9. - PubMed
-
- Kyriakides C, Wang Y, Austen WG, et al. Moderation of skeletal muscle reperfusion injury by a sLe(x)-glycosylated complement inhibitory protein. Am J Physiol, Cell Physiol 2001; 281: C224-30. - PubMed
-
- Thiagarajan RR, Winn RK, Harlan JM. The role of leukocyte and endothelial adhesion molecules in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Thromb Haemost 1997; 78: 310-4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
