A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Outcomes for Type 1 Diabetes after Bariatric Surgery
- PMID: 27375900
- PMCID: PMC4916288
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/6170719
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Outcomes for Type 1 Diabetes after Bariatric Surgery
Abstract
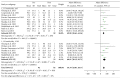
Background. The utility of bariatric surgery in type 1 diabetes remains controversial. The aim of the present study is to evaluate glycemic control outcomes in obese patients with type 1 diabetes after bariatric surgery. Methods. A comprehensive search of electronic databases was completed. Inclusion criteria included human adult subjects with BMI ≥35 kg/m(2) and a confirmed diagnosis of type 1 diabetes who underwent a bariatric surgical procedure. Results. Thirteen primary studies (86 patients) were included. Subjects had a mean age of 41.16 ± 6.76 years with a mean BMI of 42.50 ± 2.65 kg/m(2). There was a marked reduction in BMI postoperatively at 12 months and at study endpoint to 29.55 ± 1.76 kg/m(2) (P < 0.00001) and 30.63 ± 2.09 kg/m(2) (P < 0.00001), respectively. Preoperative weighted mean total daily insulin requirement was 98 ± 26 IU/d, which decreased significantly to 36 ± 15 IU/d (P < 0.00001) and 42 ± 11 IU/d (P < 0.00001) at 12 months and at study endpoint, respectively. An improvement in HbA1c was also seen from 8.46 ± 0.78% preoperatively to 7.95 ± 0.55% (P = 0.01) and 8.13 ± 0.86% (P = 0.03) at 12 months and at study endpoint, respectively. Conclusion. Bariatric surgery in patients with type 1 diabetes leads to significant reductions in BMI and improvements in glycemic control.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

