Affinity and dose of TCR engagement yield proportional enhancer and gene activity in CD4+ T cells
- PMID: 27376549
- PMCID: PMC4931909
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.10134
Affinity and dose of TCR engagement yield proportional enhancer and gene activity in CD4+ T cells
Abstract
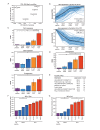
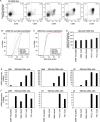
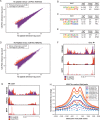
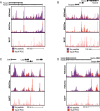
Affinity and dose of T cell receptor (TCR) interaction with antigens govern the magnitude of CD4+ T cell responses, but questions remain regarding the quantitative translation of TCR engagement into downstream signals. We find that while the response of mouse CD4+ T cells to antigenic stimulation is bimodal, activated cells exhibit analog responses proportional to signal strength. Gene expression output reflects TCR signal strength, providing a signature of T cell activation. Expression changes rely on a pre-established enhancer landscape and quantitative acetylation at AP-1 binding sites. Finally, we show that graded expression of activation genes depends on ERK pathway activation, suggesting that an ERK-AP-1 axis plays an important role in translating TCR signal strength into proportional activation of enhancers and genes essential for T cell function.
Keywords: computational biology; enhancers; immunology; mouse; protein kinase; systems biology; transcription factors.
Conflict of interest statement
CKG: Reviewing editor,
The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures











References
-
- Alexander J. Functional consequences of engagement of the T cell receptor by low affinity ligands. Journal of Immunology. 1993;150:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Allison KA. homer-idr: Second pass updated. 2015 doi: 10.5281/zenodo.17163. - DOI
-
- Anderson MK, Hernandez-Hoyos G, Diamond RA, Rothenberg EV. Precise developmental regulation of Ets family transcription factors during specification and commitment to the T cell lineage. Development. 1999;126:3131–3148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI103440/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA010815/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK091183/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA023100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM085764/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AI112269/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009523/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK074868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA173903/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI073885/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK095008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

