Radiotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: New Indications and Directions for Future Study
- PMID: 27377923
- PMCID: PMC6279296
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djw133
Radiotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: New Indications and Directions for Future Study
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cause of cancer death worldwide; its incidence is increasing in the United States. Depending on disease extent and underlying liver status, patients may be treated with local, locoregional, and/or systemic therapy. Recent data indicates that radiotherapy (RT) can play a meaningful role in the management of HCC. Here, we review published experiences using RT for HCC, including the use of radiosensitizers and stereotactic RT. We discuss methods for performing preclinical studies of RT for HCC and biomarkers of response. As a part of the HCC Working Group, an informal committee of the National Cancer Institute's Radiation Research Program, we suggest how RT should be implemented in the management of HCC and identify future directions for the study of RT in HCC.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
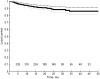
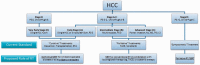
References
-
- Ferenci P, Fried M, Labrecque D , et al. . World Gastroenterology Organisation Guideline. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): a global perspective . J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2010. ; 19 ( 3 ): 311 – 317 . - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM , et al. . Global cancer statistics . CA Cancer J Clin. 2011. ; 61 ( 2 ): 69 – 90 . - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V , et al. . Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma . N Engl J Med. 2008. ; 359 ( 4 ): 378 – 390 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

