Transanal total mesorectal excision (taTME) for rectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of oncological and perioperative outcomes compared with laparoscopic total mesorectal excision
- PMID: 27377924
- PMCID: PMC4932707
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-016-2428-5
Transanal total mesorectal excision (taTME) for rectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of oncological and perioperative outcomes compared with laparoscopic total mesorectal excision
Abstract
Background: Transanal total mesorectal excision (taTME) is an emerging surgical technique for rectal cancer. However, the oncological and perioperative outcomes are controversial when compared with conventional laparoscopic total mesorectal excision (laTME).
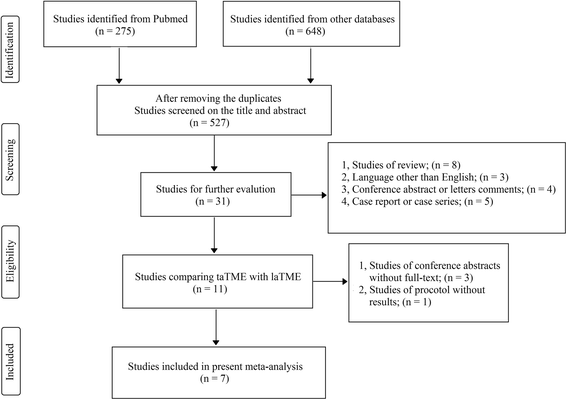
Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis based on Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines was conducted in PubMed, Embase and Cochrane database. All original studies published in English that compared taTME with laTME were included for critical appraisal and meta-analysis. Data synthesis and statistical analysis were carried out using RevMan 5.3 software.
Results: A total of seven studies including 573 patients (taTME group = 270; laTME group = 303) were included in our meta-analysis. Concerning the oncological outcomes, no differences were observed in harvested lymph nodes, distal resection margin (DRM) and positive DRM between the two groups. However, the taTME group showed a higher rate of achievement of complete grading of mesorectal quality (OR = 1.75, 95% CI = 1.02-3.01, P = 0.04), a longer circumferential resection margin (CRM) and less involvement of positive CRM (CRM: WMD = 0.96, 95% CI = 0.60-1.31, P <0.01; positive CRM: OR = 0.39, 95% CI = 0.17-0.86, P = 0.02). Concerning the perioperative outcomes, the results for hospital stay, intraoperative complications and readmission were comparable between the two groups. However, the taTME group showed shorter operation times (WMD = -23.45, 95% CI = -37.43 to -9.46, P <0.01), a lower rate of conversion (OR = 0.29, 95% CI = 0.11-0.81, P = 0.02) and a higher rate of mobilization of the splenic flexure (OR = 2.34, 95% CI = 0.99-5.54, P = 0.05). Although the incidence of anastomotic leakage, ileus and urinary morbidity showed no difference between the groups, a significantly lower rate of overall postoperative complications (OR = 0.65, 95% CI = 0.45-0.95, P = 0.03) was observed in the taTME group.
Conclusions: In comparison with laTME, taTME seems to achieve comparable technical success with acceptable oncologic and perioperative outcomes. However, multicenter randomized controlled trials are required to further evaluate the efficacy and safety of taTME.
Keywords: Laparoscopic TME; Rectal cancer; Short-term outcomes; Transanl TME.
Figures



Comment in
-
Commentary on "Transanal total mesorectal excision (taTME) for rectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of oncological and perioperative outcomes compared with laparoscopic total mesorectal excision", published in BMC Cancer 2016 Jul 4;16(1):380. doi:10.1186/s12885-016-2428-5.Tech Coloproctol. 2016 Nov;20(11):799-800. doi: 10.1007/s10151-016-1534-3. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Tech Coloproctol. 2016. PMID: 27669710 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jeong SY, Park JW, Nam BH, Kim S, Kang SB, Lim SB, et al. Open versus laparoscopic surgery for mid-rectal or low-rectal cancer after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (COREAN trial): survival outcomes of an open-label, non-inferiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(7):767–74. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70205-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kang SB, Park JW, Jeong SY, Nam BH, Choi HS, Kim DW, et al. Open versus laparoscopic surgery for mid or low rectal cancer after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (COREAN trial): short-term outcomes of an open-label randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(7):637–45. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70131-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

