Cloud storage for endosomes
- PMID: 27378788
- PMCID: PMC5010045
- DOI: 10.15252/embj.201695080
Cloud storage for endosomes
Abstract
Coordinated regulation of vesicle trafficking is critical for the proper functioning of a cell. The bulk of cellular transport vesicles are sequestered in a “perinuclear cloud”, with only a small fraction released to the cell periphery. Jongsma et al (2016) found that the
Figures
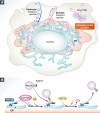
Comment on
-
An ER-Associated Pathway Defines Endosomal Architecture for Controlled Cargo Transport.Cell. 2016 Jun 30;166(1):152-66. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.078. Cell. 2016. PMID: 27368102 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Helle SC, Kanfer G, Kolar K, Lang A, Michel AH, Kornmann B (2013) Organization and function of membrane contact sites. Biochim Biophys Acta 1833: 2526–2541 - PubMed
-
- Puertollano R (2006) Endocytic trafficking and human diseases In Endosomes, Dikic I. (ed.), Vol. 10, pp 119–131. New York: Springer;
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

