Effects of electroacupuncture in a mouse model of fibromyalgia: role of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and related mechanisms
- PMID: 27381504
- PMCID: PMC5466914
- DOI: 10.1136/acupmed-2015-010986
Effects of electroacupuncture in a mouse model of fibromyalgia: role of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and related mechanisms
Abstract
Objective: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) activation and downstream transduction pathways are crucial for pain signalling. Fibromyalgia (FM) is a common pain syndrome of unclear aetiology that is often drug-refractory but may benefit from treatment with electroacupuncture (EA). We examined the contributions of NMDAR signalling to FM pain and EA responses in a mouse model.
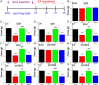
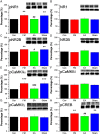
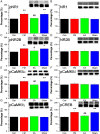
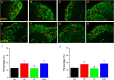
Methods: A model of FM was established by acid saline injection in 32 mice and subgroups (n=8 each) were treated with EA (2 Hz, 15 min daily for 4 days) or minimal acupuncture (MA). Expression of NMDAR subunits, calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), cyclic AMP response element binding protein (pCREB) and their corresponding phospho-activated forms were measured by Western blotting and immunohistochemistry.
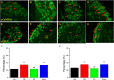
Results: Acid saline injection induced significant mechanical hyperalgesia (paw withdrawal threshold 2.18±0.27 g, p<0.05 vs controls), which was reversed by EA (4.23±0.33 g, p<0.05 vs FM group) but not by MA (2.37±0.14 g, p<0.05 vs EA group). Expression levels of phosphorylated N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (pNR)1 and pNR2B were significantly increased in the dorsal root ganglion of FM model mice (132.21±14.4% and 116.69±3.22% of control values), whereas NR1 and NR2B levels were unchanged (97.31±3.79% and 97.07%±2.27%, respectively). Expression levels of pCaMKIIα and pCREB were also higher in the FM group, and these changes were reversed by EA but not by MA. Similar changes in expression were observed in spinal cord neurons.
Conclusions: Reduced NMDAR-CaMKIIα-pCREB signalling is implicated in the positive effects of EA in FM. NMDAR signalling components may represent promising therapeutic targets for FM treatment.
Keywords: ACUPUNCTURE; ANAESTHETICS.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of ASIC3, Nav1.7 and Nav1.8 in electroacupuncture-induced analgesia in a mouse model of fibromyalgia pain.Acupunct Med. 2018 Apr;36(2):110-116. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2016-011244. Epub 2018 Jan 17. Acupunct Med. 2018. PMID: 29343477
-
Synergistic antinociceptive effects of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist and electroacupuncture in the complete Freund's adjuvant-induced pain model.Int J Mol Med. 2011 Oct;28(4):669-75. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2011.728. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Int J Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21687934
-
Analgesic Effect of Electroacupuncture in a Mouse Fibromyalgia Model: Roles of TRPV1, TRPV4, and pERK.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 4;10(6):e0128037. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128037. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26043006 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture for Fibromyalgia: A Review Based on Multidimensional Evidence.Am J Chin Med. 2023;51(2):249-277. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X23500143. Epub 2023 Jan 4. Am J Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 36599648 Review.
-
Mechanisms of acupuncture-electroacupuncture on persistent pain.Anesthesiology. 2014 Feb;120(2):482-503. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000101. Anesthesiology. 2014. PMID: 24322588 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Electroacupuncture Attenuates CFA-induced Inflammatory Pain by suppressing Nav1.8 through S100B, TRPV1, Opioid, and Adenosine Pathways in Mice.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 13;7:42531. doi: 10.1038/srep42531. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28211895 Free PMC article.
-
Distal Electroacupuncture at the LI4 Acupoint Reduces CFA-Induced Inflammatory Pain via the Brain TRPV1 Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 10;20(18):4471. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184471. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31510092 Free PMC article.
-
Electric Stimulation of Ear Reduces the Effect of Toll-Like Receptor 4 Signaling Pathway on Kainic Acid-Induced Epileptic Seizures in Rats.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Feb 26;2018:5407256. doi: 10.1155/2018/5407256. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29682548 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting ASIC3 for Relieving Mice Fibromyalgia Pain: Roles of Electroacupuncture, Opioid, and Adenosine.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 25;7:46663. doi: 10.1038/srep46663. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28440280 Free PMC article.
-
Eicosapentaenoic Acid Modulates Transient Receptor Potential V1 Expression in Specific Brain Areas in a Mouse Fibromyalgia Pain Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 1;25(5):2901. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052901. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474148 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

