Zofenopril Protects Against Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Increasing Nitric Oxide and Hydrogen Sulfide Bioavailability
- PMID: 27381758
- PMCID: PMC5015391
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.116.003531
Zofenopril Protects Against Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Increasing Nitric Oxide and Hydrogen Sulfide Bioavailability
Abstract
Background: Zofenopril, a sulfhydrylated angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI), reduces mortality and morbidity in infarcted patients to a greater extent than do other ACEIs. Zofenopril is a unique ACEI that has been shown to increase hydrogen sulfide (H2S) bioavailability and nitric oxide (NO) levels via bradykinin-dependent signaling. Both H2S and NO exert cytoprotective and antioxidant effects. We examined zofenopril effects on H2S and NO bioavailability and cardiac damage in murine and swine models of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury.
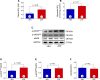
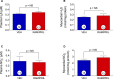
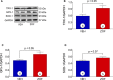
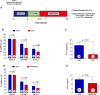
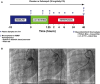
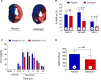
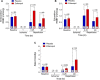
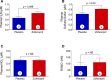
Methods and results: Zofenopril (10 mg/kg PO) was administered for 1, 8, and 24 hours to establish optimal dosing in mice. Myocardial and plasma H2S and NO levels were measured along with the levels of H2S and NO enzymes (cystathionine β-synthase, cystathionine γ-lyase, 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfur transferase, and endothelial nitric oxide synthase). Mice received 8 hours of zofenopril or vehicle pretreatment followed by 45 minutes of ischemia and 24 hours of reperfusion. Pigs received placebo or zofenopril (30 mg/daily orally) 7 days before 75 minutes of ischemia and 48 hours of reperfusion. Zofenopril significantly augmented both plasma and myocardial H2S and NO levels in mice and plasma H2S (sulfane sulfur) in pigs. Cystathionine β-synthase, cystathionine γ-lyase, 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfur transferase, and total endothelial nitric oxide synthase levels were unaltered, while phospho-endothelial nitric oxide synthase(1177) was significantly increased in mice. Pretreatment with zofenopril significantly reduced myocardial infarct size and cardiac troponin I levels after I/R injury in both mice and swine. Zofenopril also significantly preserved ischemic zone endocardial blood flow at reperfusion in pigs after I/R.
Conclusions: Zofenopril-mediated cardioprotection during I/R is associated with an increase in H2S and NO signaling.
Keywords: antihypertensive agent; hydrogen sulfide; myocardial ischemia; nitric oxide; oxidant stress; troponin.
© 2016 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures

References
-
- Indications for ACE inhibitors in the early treatment of acute myocardial infarction: systematic overview of individual data from 100,000 patients in randomized trials. ACE Inhibitor Myocardial Infarction Collaborative Group. Circulation. 1998;97:2202–2212. - PubMed
-
- Flather MD, Yusuf S, Kober L, Pfeffer M, Hall A, Murray G, Torp‐Pedersen C, Ball S, Pogue J, Moye L, Braunwald E. Long‐term ACE‐inhibitor therapy in patients with heart failure or left‐ventricular dysfunction: a systematic overview of data from individual patients. ACEInhibitor Myocardial Infarction Collaborative Group. Lancet. 2000;355:1575–1581. - PubMed
-
- Rodrigues EJ, Eisenberg MJ, Pilote L. Effects of early and late administration of angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitors on mortality after myocardial infarction. Am J Med. 2003;115:473–479. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

