In Primary Aldosteronism, Mineralocorticoids Influence Exosomal Sodium-Chloride Cotransporter Abundance
- PMID: 27381844
- PMCID: PMC5198275
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2015111221
In Primary Aldosteronism, Mineralocorticoids Influence Exosomal Sodium-Chloride Cotransporter Abundance
Abstract
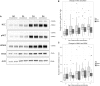
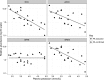
Distal tubular sodium retention is a potent driver of hypertension, and the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride cotransporter (NCC) has a key role in this process. In humans, factors regulating NCC are unclear, but in animal models, aldosterone is a potent regulator, possibly via effects on plasma potassium. We studied the effects of the mineralocorticoid fludrocortisone on the abundance of NCC and its phosphorylated form (pNCC) as well as WNK lysine deficient protein kinase 4 (WNK4) and STE20/SPS1-related, proline alanine-rich kinase (SPAK) in human urinary exosomes. We isolated exosomes from daily urine samples in 25 patients undergoing fludrocortisone suppression testing (100 μg every 6 hours for 4 days) to diagnose or exclude primary aldosteronism. Over the course of the test, NCC levels increased 3.68-fold (P<0.01) and pNCC levels increased 2.73-fold (P<0.01) relative to baseline. The ratio of pNCC/NCC dropped by 48% (P<0.01). The abundance of WNK4 increased 3.23-fold (P<0.01), but SPAK abundance did not change significantly (P=0.14). Plasma potassium concentration strongly and negatively correlated with pNCC, NCC, and WNK4 abundance (P<0.001 for all). This study shows that, in humans, mineralocorticoid administration is associated with a rapid increase in abundance of NCC and pNCC, possibly via the WNK pathway. These effects may be driven by changes in plasma potassium.
Keywords: Exosomes; NCC; Na transport; aldosterone.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The phosphorylated sodium chloride cotransporter in urinary exosomes is superior to prostasin as a marker for aldosteronism.Hypertension. 2012 Sep;60(3):741-8. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.198135. Epub 2012 Jul 30. Hypertension. 2012. PMID: 22851731
-
Chronic Metabolic Acidosis Activates Renal Tubular Sodium Chloride Cotransporter through Angiotension II-dependent WNK4-SPAK Phosphorylation Pathway.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 5;6:18360. doi: 10.1038/srep18360. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26728390 Free PMC article.
-
Aldosterone modulates thiazide-sensitive sodium chloride cotransporter abundance via DUSP6-mediated ERK1/2 signaling pathway.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015 May 15;308(10):F1119-27. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00543.2014. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25761881 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular physiology of the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride cotransporter.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2009 Sep;18(5):421-7. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e32832f2fcb. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2009. PMID: 19636250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular insights from dysregulation of the thiazide-sensitive WNK/SPAK/NCC pathway in the kidney: Gordon syndrome and thiazide-induced hyponatraemia.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2013 Dec;40(12):876-84. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12115. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23683032 Review.
Cited by
-
Urinary extracellular vesicles: A position paper by the Urine Task Force of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.J Extracell Vesicles. 2021 May;10(7):e12093. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12093. Epub 2021 May 21. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021. PMID: 34035881 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms for the modulation of blood pressure and potassium homeostasis by the distal convoluted tubule.EMBO Mol Med. 2022 Feb 7;14(2):e14273. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202114273. Epub 2021 Dec 20. EMBO Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34927382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urinary Extracellular Vesicle Protein Profiling and Endogenous Lithium Clearance Support Excessive Renal Sodium Wasting and Water Reabsorption in Thiazide-Induced Hyponatremia.Kidney Int Rep. 2018 Sep 22;4(1):139-147. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2018.09.011. eCollection 2019 Jan. Kidney Int Rep. 2018. PMID: 30596177 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Intravenous NaCl and Volume Expansion Reduces Sodium-Chloride Cotransporter Abundance and Phosphorylation in Urinary Extracellular Vesicles.Kidney360. 2022 Mar 1;3(5):910-921. doi: 10.34067/KID.0000362022. eCollection 2022 May 26. Kidney360. 2022. PMID: 36128481 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the alternative splice variant of NCC in blood pressure control.Channels (Austin). 2018;12(1):346-355. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2018.1528820. Channels (Austin). 2018. PMID: 30264650 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lifton RP, Gharavi AG, Geller DS: Molecular mechanisms of human hypertension. Cell 104: 545–556, 2001 - PubMed
-
- O’Shaughnessy KM: Gordon Syndrome: A continuing story. Pediatr Nephrol 30: 1903–1908, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Golbang AP, Murthy M, Hamad A, Liu CH, Cope G, Van’t Hoff W, Cuthbert A, O’Shaughnessy KM: A new kindred with pseudohypoaldosteronism type II and a novel mutation (564D>H) in the acidic motif of the WNK4 gene. Hypertension 46: 295–300, 2005 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

