A Nonoligomerizing Mutant Form of Helicobacter pylori VacA Allows Structural Analysis of the p33 Domain
- PMID: 27382020
- PMCID: PMC4995914
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00254-16
A Nonoligomerizing Mutant Form of Helicobacter pylori VacA Allows Structural Analysis of the p33 Domain
Abstract
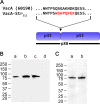
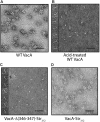
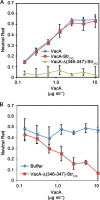
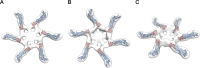
Helicobacter pylori secretes a pore-forming VacA toxin that has structural features and activities substantially different from those of other known bacterial toxins. VacA can assemble into multiple types of water-soluble flower-shaped oligomeric structures, and most VacA activities are dependent on its capacity to oligomerize. The 88-kDa secreted VacA protein can undergo limited proteolysis to yield two domains, designated p33 and p55. The p33 domain is required for membrane channel formation and intracellular toxic activities, and the p55 domain has an important role in mediating VacA binding to cells. Previous studies showed that the p55 domain has a predominantly β-helical structure, but no structural data are available for the p33 domain. We report here the purification and analysis of a nonoligomerizing mutant form of VacA secreted by H. pylori The nonoligomerizing 88-kDa mutant protein retains the capacity to enter host cells but lacks detectable toxic activity. Analysis of crystals formed by the monomeric protein reveals that the β-helical structure of the p55 domain extends into the C-terminal portion of p33. Fitting the p88 structural model into an electron microscopy map of hexamers formed by wild-type VacA (predicted to be structurally similar to VacA membrane channels) reveals that p55 and the β-helical segment of p33 localize to peripheral arms but do not occupy the central region of the hexamers. We propose that the amino-terminal portion of p33 is unstructured when VacA is in a monomeric form and that it undergoes a conformational change during oligomer assembly.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

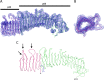
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 GM008320/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R25 GM062459/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007281/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA116087/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI118932/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI039657/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR026915/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007751/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AI112324/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX000627/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 AI108778/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

