Endocrine Abnormalities in Aging Survivors of Childhood Cancer: A Report From the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study
- PMID: 27382091
- PMCID: PMC5024546
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2016.66.6545
Endocrine Abnormalities in Aging Survivors of Childhood Cancer: A Report From the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study
Abstract
Purpose: The development of endocrinopathies in survivors of childhood cancer as they age remains understudied. We characterized endocrine outcomes in aging survivors from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study on the basis of therapeutic exposures.
Patients and methods: We analyzed self-reported conditions in 14,290 5-year survivors from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study, with a median age 6 years (range, < 1 to 20 years) at diagnosis and 32 years (range, 5 to 58 years) at last follow-up. Identification of high-risk therapeutic exposures was adopted from the Children's Oncology Group Long-Term Follow-Up Guidelines. Cumulative incidence curves and prevalence estimates quantified and regression models compared risks of primary hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, thyroid neoplasms, hypopituitarism, obesity, diabetes mellitus, or gonadal dysfunction between survivors and siblings.
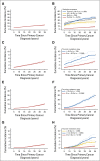
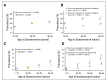
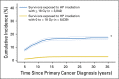
Results: The cumulative incidence and prevalence of endocrine abnormalities increased across the lifespan of survivors (P < .01 for all). Risk was significantly higher in survivors exposed to high-risk therapies compared with survivors not so exposed for primary hypothyroidism (hazard ratio [HR], 6.6; 95% CI, 5.6 to 7.8), hyperthyroidism (HR, 1.8; 95% CI, 1.2 to 2.8), thyroid nodules (HR, 6.3; 95% CI, 5.2 to 7.5), thyroid cancer (HR, 9.2; 95% CI, 6.2 to 13.7), growth hormone deficiency (HR, 5.3; 95% CI, 4.3 to 6.4), obesity (relative risk, 1.8; 95% CI, 1.7 to 2.0), and diabetes mellitus (relative risk, 1.9; 95% CI, 1.6 to 2.4). Women exposed to high-risk therapies had six-fold increased risk for premature ovarian insufficiency (P < .001), and men demonstrated higher prevalence of testosterone replacement (P < .001) after cyclophosphamide equivalent dose of 20 g/m(2) or greater or testicular irradiation with 20 Gy or greater. Survivors demonstrated an increased risk for all thyroid disorders and diabetes mellitus regardless of treatment exposures compared with siblings (P < .001 for all).
Conclusion: Endocrinopathies in survivors increased substantially over time, underscoring the need for lifelong subspecialty follow-up of those at risk.
© 2016 by American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ disclosures of potential conflicts of interest are found in the article online at www.jco.org. Author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures



Comment in
-
When Do Late Effects in Childhood Cancer Survivors Cease Emerging? The Endocrine Answer.J Clin Oncol. 2016 Sep 20;34(27):3231-2. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.68.9232. Epub 2016 Aug 1. J Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27480146 No abstract available.
-
Disease watch: Optimizing endocrine care for survivors of childhood cancer.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016 Oct;12(10):564-5. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2016.152. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27585962 No abstract available.
References
-
- National Cancer Institute SEER Data, 1973-2013. http://seer.cancer.gov/data/
-
- Oeffinger KC, Mertens AC, Sklar CA, et al. Chronic health conditions in adult survivors of childhood cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1572–1582. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

