CALGB 80403 (Alliance)/E1206: A Randomized Phase II Study of Three Chemotherapy Regimens Plus Cetuximab in Metastatic Esophageal and Gastroesophageal Junction Cancers
- PMID: 27382098
- PMCID: PMC5019745
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2015.65.5092
CALGB 80403 (Alliance)/E1206: A Randomized Phase II Study of Three Chemotherapy Regimens Plus Cetuximab in Metastatic Esophageal and Gastroesophageal Junction Cancers
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the optimal chemotherapy backbone for testing in future US cooperative group studies for metastatic esophageal and gastroesophageal junction cancers. Cetuximab was added to each treatment arm based on promising preclinical data.
Patients and methods: Patients with previously untreated metastatic esophageal or gastroesophageal junction cancer were randomly assigned at a one-to-one-to-one ratio to epirubicin, cisplatin, and continuous-infusion fluorouracil (ECF), irinotecan plus cisplatin (IC), or FOLFOX (oxaliplatin, leucovorin, and bolus and infusional fluorouracil). All treatment programs included cetuximab once per week. The primary end point was response rate. Secondary outcomes included overall survival, progression-free survival, time to treatment failure, and safety. As prespecified, primary and secondary analyses were conducted only among patients with adenocarcinoma.
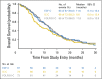
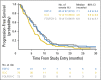
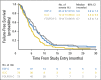
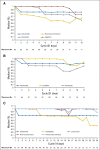
Results: This study randomly assigned 245 patients, including 222 with adenocarcinoma. Among patients with adenocarcinoma, response rate was 60.9% (95% CI, 47.9 to 72.8) for ECF plus cetuximab, 45.0% (95% CI, 33.0 to 57.0) for IC plus cetuximab, and 54.3% (95% CI, 42.0 to 66.2) for FOLFOX plus cetuximab. Median overall survival was 11.6, 8.6, and 11.8 months; median progression-free survival was 7.1, 4.9, and 6.8 months; and median time to treatment failure was 5.6, 4.3, and 6.7 months for each of these arms, respectively. FOLFOX plus cetuximab required fewer treatment modifications compared with ECF plus cetuximab and IC plus cetuximab (P = .013), and fewer patients were removed from treatment because of an adverse event or experienced treatment-related death.
Conclusion: In combination with cetuximab, ECF and FOLFOX had similar efficacy, but FOLFOX was better tolerated. Although differences were nonsignificant, IC plus cetuximab seemed to be the least effective and most toxic of the three regimens tested.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00381706.
© 2016 by American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ disclosures of potential conflicts of interest are found in the article online at www.jco.org. Author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

Comment in
-
It Is Time to Stop Using Epirubicin to Treat Any Patient With Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma.J Clin Oncol. 2017 Feb;35(4):475-477. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.69.7276. Epub 2016 Oct 28. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28129519 No abstract available.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Chau I, Norman AR, Cunningham D, et al. Multivariate prognostic factor analysis in locally advanced and metastatic esophago-gastric cancer: Pooled analysis from three multicenter, randomized, controlled trials using individual patient data. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:2395–2403. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham D, Starling N, Rao S, et al. Capecitabine and oxaliplatin for advanced esophagogastric cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:36–46. - PubMed
-
- Van Cutsem E, Moiseyenko VM, Tjulandin S, et al. Phase III study of docetaxel and cisplatin plus fluorouracil compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil as first-line therapy for advanced gastric cancer: A report of the V325 Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4991–4997. - PubMed
-
- Dank M, Zaluski J, Barone C, et al. Randomized phase III study comparing irinotecan combined with 5-fluorouracil and folinic acid to cisplatin combined with 5-fluorouracil in chemotherapy naive patients with advanced adenocarcinoma of the stomach or esophagogastric junction. Ann Oncol. 2008;19:1450–1457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U10 CA180836/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180866/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189858/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180854/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA006927/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA021115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA031946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189819/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA196172/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180838/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180850/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189829/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180791/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189853/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

