Implementation and evaluation of a pharmacist-led hypertension management service in primary care: outcomes and methodological challenges
- PMID: 27382427
- PMCID: PMC4930861
- DOI: 10.18549/PharmPract.2016.02.723
Implementation and evaluation of a pharmacist-led hypertension management service in primary care: outcomes and methodological challenges
Abstract
Background: Suboptimal utilisation of pharmacotherapy, non-adherence to prescribed treatment, and a lack of monitoring all contribute to poor blood (BP) pressure control in patients with hypertension.
Objective: The objective of this study was to evaluate the implementation of a pharmacist-led hypertension management service in terms of processes, outcomes, and methodological challenges.
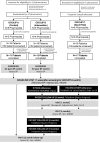
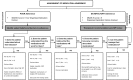
Method: A prospective, controlled study was undertaken within the Australian primary care setting. Community pharmacists were recruited to one of three study groups: Group A (Control - usual care), Group B (Intervention), or Group C (Short Intervention). Pharmacists in Groups B and C delivered a service comprising screening and monitoring of BP, as well as addressing poor BP control through therapeutic adjustment and adherence strategies. Pharmacists in Group C delivered the shortened version of the service.
Results: Significant changes to key outcome measures were observed in Group C: reduction in systolic and diastolic BPs at the 3-month visit (P<0.01 and P<0.01, respectively), improvement in medication adherence scores (P=0.01), and a slight improvement in quality of life (EQ-5D-3L Index) scores (P=0.91). There were no significant changes in Group B (the full intervention), and no differences in comparison to Group A (usual care). Pharmacists fed-back that patient recruitment was a key barrier to service implementation, highlighting the methodological implications of screening.
Conclusion: A collaborative, pharmacist-led hypertension management service can help monitor BP, improve medication adherence, and optimise therapy in a step-wise approach. However, blood pressure screening can effect behaviour change in patients, presenting methodological challenges in the evaluation of services in this context.
Keywords: Australia; Community Pharmacy Services; Hypertension; Interprofessional Relations; Medication Adherence; Medication Therapy Management; Methodology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chow CK, Teo KK, Rangarajan S, Islam S, Gupta R, Avezum A, Bahonar A, Chifamba J, Dagenais G, Diaz R, Kazmi K, Lanas F, Wei L, Lopez-Jaramillo P, Fanghong L, Ismail NH, Puoane T, Rosengren A, Szuba A, Temizhan A, Wielgosz A, Yusuf R, Yusufali A, McKee M, Liu L, Mony P, Yusuf S PURE (Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology) Study investigators. PRevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in rural and urban communities in high-, middle-, and low-income countries. JAMA. 2013;310(9):959–968. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.184182. - PubMed
-
- Ho PM, Magid DJ, Shetterly SM, Olson KL, Peterson PN, Masoudi FA, Rumsfeld JS. Importance of therapy intensification and medication nonadherence for blood pressure control in patients with coronary disease. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168(3):271–276. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2007.72. - PubMed
-
- Janus ED, Bunker SJ, Kilkkinen A, Mc Namara K, Philpot B, Tideman P, Tirimacco R, Laatikainen TK, Heistaro S, Dunbar JA. Prevalence, detection and drug treatment of hypertension in a rural Australian population: the Greater Green Triangle risk factor study 2004-2006. Intern Med J. 2008;38(12):879–886. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.2007.01583.x. - PubMed
-
- Peterson G, Jackson S, Hughes J, Fitzmaurice K, Murphy L. Public perceptions of the role of Australian pharmacists in cardiovascular disease. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2010;35(6):671–677. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2710.2009.01139.x. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
