Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Micro-Malignant Melanoma Lesions Applying Support Vector Machines
- PMID: 27382567
- PMCID: PMC4921724
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/4381972
Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Micro-Malignant Melanoma Lesions Applying Support Vector Machines
Abstract
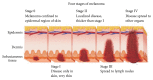
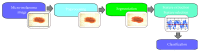
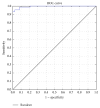
Background. One of the fatal disorders causing death is malignant melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer. The aim of the modern dermatology is the early detection of skin cancer, which usually results in reducing the mortality rate and less extensive treatment. This paper presents a study on classification of melanoma in the early stage of development using SVMs as a useful technique for data classification. Method. In this paper an automatic algorithm for the classification of melanomas in their early stage, with a diameter under 5 mm, has been presented. The system contains the following steps: image enhancement, lesion segmentation, feature calculation and selection, and classification stage using SVMs. Results. The algorithm has been tested on 200 images including 70 melanomas and 130 benign lesions. The SVM classifier achieved sensitivity of 90% and specificity of 96%. The results indicate that the proposed approach captured most of the malignant cases and could provide reliable information for effective skin mole examination. Conclusions. Micro-melanomas due to the small size and low advancement of development create enormous difficulties during the diagnosis even for experts. The use of advanced equipment and sophisticated computer systems can help in the early diagnosis of skin lesions.
Figures



References
-
- Argenziano G., Soyer H. P., De Giorgio V., et al. Interactive Atlas of Dermoscopy (Book and CD-ROM) Milano, Italy: Edra Medical Publishing and New Media; 2000.
-
- Malignant melanoma. 2015, http://www.dermatology.ca/skin-hair-nails/skin/skin-cancer/malignant-mel...
-
- Schmoeckel C. Small malignant melanomas: clinicopathologic correlation and DNA ploidy analysis. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 1991;24(6, part 1):1036–1037. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

