New insights into cell non-autonomous mechanisms of the C. elegans hypoxic response
- PMID: 27383456
- PMCID: PMC4911976
- DOI: 10.1080/21624054.2016.1176823
New insights into cell non-autonomous mechanisms of the C. elegans hypoxic response
Abstract
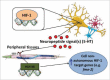
The hypoxic response is a well-studied and highly conserved biological response to low oxygen availability. First described more than 20 y ago, the traditional model for this response is that declining oxygen levels lead to stabilization of hypoxia-inducible transcription factors (HIFs), which then bind to hypoxia responsive elements (HREs) in target genes to mediate the transcriptional changes collectively known as the hypoxic response.(1,2) Recent work in C. elegans has forced a re-evaluation of this model by indicating that the worm HIF (HIF-1) can mediate effects in a cell non-autonomous fashion and, in at least one case, increase expression of an intestinal hypoxic response target gene in cells lacking HIF-1.
Keywords: aging; flavin-containing monooxygenase; hypoxic signaling; longevity; serotonin.
Figures
Comment on
-
Cell nonautonomous activation of flavin-containing monooxygenase promotes longevity and health span.Science. 2015 Dec 11;350(6266):1375-1378. doi: 10.1126/science.aac9257. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Science. 2015. PMID: 26586189 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang GL, Semenza GL. General involvement of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in transcriptional response to hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1993; 90:4304-8; PMID:8387214; http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.90.9.4304 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA, Semenza GL. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1995; 92:5510-4; PMID:7539918; http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.12.5510 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kallio PJ, Wilson WJ, O'Brien S, Makino Y, Poellinger L. Regulation of the hypoxia-inducible transcription factor 1alpha by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. J Biol Chem 1999; 274:6519-25; PMID:10037745; http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.10.6519 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bishop T, Lau KW, Epstein AC, Kim SK, Jiang M, O'Rourke D, Pugh CW, Gleadle JM, Taylor MS, Hodgkin J, et al.. Genetic analysis of pathways regulated by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Biol 2004; 2:e289; PMID:15361934; http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0020289 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Epstein ACR, Gleadle JM, McNeill LA, Hewitson KS, O'Rourke J, Mole DR, Mukherji M, Metzen E, Wilson MI, Dhanda A, et al.. C. elegans EGL-9 and Mammalian Homologs Define a Family of Dioxygenases that Regulate HIF by Prolyl Hydroxylation. Cell 2001; 107:43-54; PMID:11595184; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00507-4 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
