Effects of budlein A on human neutrophils and lymphocytes
- PMID: 27383709
- PMCID: PMC5022217
- DOI: 10.1590/1678-775720150540
Effects of budlein A on human neutrophils and lymphocytes
Abstract
Objective: In this study, we evaluated whether budlein A modulates the activation of innate and adaptive immune cells such as neutrophils and lymphocytes.
Material and methods: Our research group has investigated several plant species and several compounds have been isolated, identified, and their medical potential evaluated. Budlein A is a SL isolated from the species Aldama buddlejiformis and A. robusta (Asteraceae) and shows anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive activities. Advances in understanding how plant-derived substances modulate the activation of innate and adaptive immune cells have led to the development of new therapies for human diseases.
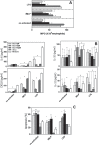
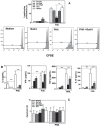
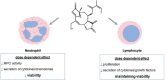
Results: Budlein A inhibited MPO activity, IL-6, CXCL8, IL-10, and IL-12 production and induces neutrophil apoptosis. In contrast, budlein A inhibited lymphocyte proliferation and IL-2, IL-10, TGF-β, and IFN-γ production, but it did not lead to cell death.
Conclusions: Collectively, our results indicate that budlein A shows distinct immunomodulatory effects on immune cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of the sesquiterpene lactone budlein A in mice: inhibition of cytokine production-dependent mechanism.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 May 7;562(1-2):155-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.01.029. Epub 2007 Feb 1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17320857
-
Budlein A from Viguiera robusta inhibits leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions, adhesion molecule expression and inflammatory mediators release.Phytomedicine. 2009 Oct;16(10):904-15. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2009.04.002. Epub 2009 Jun 12. Phytomedicine. 2009. PMID: 19524419
-
Further sesquiterpene lactones from Viguiera robusta and the potential anti-inflammatory activity of a heliangolide: inhibition of human neutrophil elastase release.Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2008 Jul-Aug;63(7-8):533-8. doi: 10.1515/znc-2008-7-811. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2008. PMID: 18810997
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Immunoregulatory Action of Sesquiterpene Lactones.Molecules. 2022 Feb 8;27(3):1142. doi: 10.3390/molecules27031142. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review on pharmacology and toxicology of Elephantopus scaber Linn.Nat Prod Res. 2014;28(11):819-30. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2014.883394. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Nat Prod Res. 2014. PMID: 24499355 Review.
Cited by
-
The Sesquiterpene Lactone, Budlein A, Inhibits Antigen-Induced Arthritis in Mice: Role of NF-κB and Cytokines.Inflammation. 2017 Dec;40(6):2020-2032. doi: 10.1007/s10753-017-0642-1. Inflammation. 2017. PMID: 28780730
-
Budlein A, a Sesquiterpene Lactone From Viguiera robusta, Alleviates Pain and Inflammation in a Model of Acute Gout Arthritis in Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Sep 25;9:1076. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01076. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30319413 Free PMC article.
-
Splenectomy protects aged mice from injury after experimental stroke.Neurobiol Aging. 2018 Jan;61:102-111. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.09.022. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Neurobiol Aging. 2018. PMID: 29059593 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arakawa NS, Schorr K, Ambrósio SR, Merfort I, Costa FB. Further sesquiterpene lactones from Viguiera robusta and the potential anti-inflammatory activity of a heliangolide: inhibition of human neutrophil elastase release. Z Naturforsch C. 2008;6:533–538. - PubMed
-
- Calixto JB, Campos MM, Otuki MF, Santos AR. Anti-inflammatory compounds of plant origin. Part II. Modulation of proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines and adhesion molecules. Planta Med. 2004;70:93–103. - PubMed
-
- Cho JY, Baik KU, Jung JH, Park MH. In vitro anti-inflammatory effects of cynaropicrin, a sesquiterpene lactone, from Saussurea lappa. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;398:399–407. - PubMed
-
- Costa FB, Schorr K, Arakawa NS, Schilling EE, Sprin GO. Infraspecific variation in the chemistry of glandular trichomes of two Brazilian Viguiera species (Heliantheae; Asteraceae) J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2001;12:403–407.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

