TNF-alpha expression, evaluation of collagen, and TUNEL of Matricaria recutita L. extract and triamcinolone on oral ulcer in diabetic rats
- PMID: 27383710
- PMCID: PMC5022216
- DOI: 10.1590/1678-775720150481
TNF-alpha expression, evaluation of collagen, and TUNEL of Matricaria recutita L. extract and triamcinolone on oral ulcer in diabetic rats
Abstract
Objective: to evaluate the influence of Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha (TNF-α) and apoptosis in rats with DM treated with chamomile extract or triamcinolone.
Material and methods: Wistar male rats (210.0±4.2 g) were divided into five groups: negative control group (NCG) without diabetes; positive control group (PCG) with DM (alloxan, 45 mg/kg); and groups treated with chamomile extract (normoglycemic= NCG group and diabetic= DCG group) and with triamcinolone (TG). Traumatic ulcers were performed on all animals that received topical triamcinolone, chamomile extract or saline 12/12 hours for ten days.
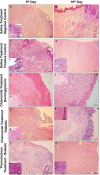
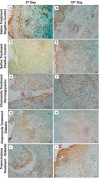
Results: On days five and ten the animals were euthanized and the ulcers were analyzed by light microscopy, TUNEL assay, and immunohistochemically (TNF-α). The NCG (p=0.0062), PCG (p=0.0285), NCG (p=0.0041), and DCG (p<0.0001) groups were completely healed on the 10th day, however, there was no healing on the TG (p=0.5127) group. The TNF-α expression showed a significant reduction from the 5th to the 10th day in NCG (p=0.0266) and DCG (p=0.0062). In connective tissue, the TUNEL assay showed a significant reduction in the number of positive cells in NCG (p=0.0273) and CNG (p=0.0469) and in the epithelium only in CDG (p=0.0320).
Conclusions: Chamomile extract can optimize the healing of traumatic oral ulcers in diabetic rats through the reduction of apoptosis in the epithelium and TNF-α expression.
Conflict of interest statement
AND SOURCE OF FUNDING The authors declare no sources of funding and conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects of Chamomilla recutita (L.) on oral wound healing in rats.Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2011 Sep 1;16(6):e716-21. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2011. PMID: 21196867
-
Dry Extract of Matricaria recutita L. (Chamomile) Prevents Ligature-Induced Alveolar Bone Resorption in Rats via Inhibition of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Interleukin-1β.J Periodontol. 2016 Jun;87(6):706-15. doi: 10.1902/jop.2016.150411. Epub 2016 Jan 16. J Periodontol. 2016. PMID: 26777767
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) blockage reduces acute inflammation and delayed wound healing in oral ulcer of rats.Inflammopharmacology. 2022 Oct;30(5):1781-1798. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-01046-3. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Inflammopharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35948810
-
An experimental study of the effects of Matricaria chamomilla extract on cutaneous burn wound healing in albino rats.Nat Prod Res. 2008 Mar 20;22(5):422-7. doi: 10.1080/14786410701591713. Nat Prod Res. 2008. PMID: 18404562
-
A review of the bioactivity and potential health benefits of chamomile tea (Matricaria recutita L.).Phytother Res. 2006 Jul;20(7):519-30. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1900. Phytother Res. 2006. PMID: 16628544 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of HGF responses to oral traumatic ulcers using an HGF-Tg mouse model.Exp Anim. 2022 May 20;71(2):204-213. doi: 10.1538/expanim.21-0141. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Exp Anim. 2022. PMID: 34819402 Free PMC article.
-
Matricaria chamomilla L. Ameliorates Asthma by Protecting OVA-Induced Rats and LPS-Induced Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells Through Suppressing Autophagy and Apoptosis.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Feb 13;13(2):e70030. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70030. eCollection 2025 Feb. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39949885 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Matricaria Recutita (L.) in the Treatment of Oral Mucositis.ScientificWorldJournal. 2018 Jun 12;2018:4392184. doi: 10.1155/2018/4392184. eCollection 2018. ScientificWorldJournal. 2018. PMID: 30008621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Activity and Wound Healing Effect of Kaempferia galanga L. Rhizome on the Chemical-Induced Oral Mucosal Ulcer in Wistar Rats.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Apr 8;15:2281-2294. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S359042. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35422649 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology and bioinformatics analyses identify the intersection genes and mechanism of Huang Bai for recurrent aphthous stomatitis.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2022 Jan-Dec;36:3946320221129134. doi: 10.1177/03946320221129134. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36189637 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alberti LR, Vasconcellos LS, Petroianu A. Influence of local or systemic corticosteroids on skin wound healing resistance. Acta Cir Bras. 2012;27(4):295–299. - PubMed
-
- Andrade TA, Iyer A, Das PK, Foss NT, Garcia SB, Coutinho-Netto J, et al. The inflammatory stimulus of a natural latex biomembrane improves healing in rats. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2011;44(10):1036–1047. - PubMed
-
- Bastos AS, Leite AR, Spin R, Neto, Nassar PO, Massucato ES, Orrico SR. Diabetes mellitus and oral mucosa alterations: prevalence and risk factors. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011;92(1):100–105. - PubMed
-
- Bedi MK, Shenefelt PD. Herbal therapy in dermatology. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138(2):232–242. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

