Tissue dissolution and modifications in dentin composition by different sodium hypochlorite concentrations
- PMID: 27383711
- PMCID: PMC5022212
- DOI: 10.1590/1678-775720150524
Tissue dissolution and modifications in dentin composition by different sodium hypochlorite concentrations
Abstract
Objectives: To determine the organic matter dissolution and changes in dentin chemical composition promoted by different concentrations of NaOCl over time.
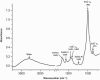
Material and methods: Fragments of bovine muscle tissue were weighed before and after 5, 10, and 15 min of immersion in the groups (n=10): G1- 0.9% saline solution; G2- 1% NaOCl; G3- 2.5% NaOCl; and G4- 5% NaOCl. Bovine dentin fragments were subjected to the same irrigants and absorption spectra were collected by Attenuated Total Reflectance of Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) before and after 0,5, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, and 10 min of immersion in the solutions. The ratios of the amide III/phosphate and carbonate/phosphate absorption bands were determined. The tissue dissolution and carbonate/phosphate ratios were submitted to the two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey's multiple-comparison test (α<0.05) and to the one-way analysis of variance with Tukey's (α<0.05). The amide III/phosphate ratio was analyzed by Friedman test (α<0.05) and the Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's post-hoc (α<0.05).
Results: The increase in NaOCl concentration and contact time intensified the dissolution of organic matter and dentin collagen with reduction in the amide III/phosphate ratio. Significant differences between all groups (p<0.05) were observed in the dissolution of organic matter at 10 min and in the amide III/phosphate ratio between the saline solution and 5% NaOCl at 5 min. The carbonate/phosphate ratio decreased significantly in G2, G3, and G4 after 0,5 min of immersion (p<0.05), but more alterations did not occur in the subsequent periods (p>0.05). Intergroup differences were not observed in this ratio (p>0.05).
Conclusions: The increase in the exposure time and in the concentration of NaOCl solution lead to an increase in the tissue dissolution and dentin collagen deproteination. Furthermore, some carbonate ions are removed from the dentin inorganic phase by the NaOCl.
Figures
References
-
- Almeida LH, Leonardo NG, Gomes AP, Giardino L, Souza EM, Pappen FG. Pulp tissue dissolution capacity of sodium hypochlorite combined with cetrimide and polypropylene glycol. Braz Dent J. 2013;24:477–481. - PubMed
-
- Atabek D, Bodur H, Yalçin G, Kalayci Ş. Effects of oxidative irrigants on root dentin structure: Attenuated Total Reflection Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy study. Oral Health Dent Manag. 2014;13:753–756. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann L, Diebolder R, Hibst R, Zezell DM. Infrared absorption bands of enamel and dentin tissues from human and bovine teeth. Appl Spectrosc Rev. 2003;38:1–14.
-
- Bloomfield SF, Miles GA. The antibacterial properties of sodium dichloroisocyanurate and sodium hypochlorite formulations. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979;46:65–73. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous