Interactions between the microbiota and pathogenic bacteria in the gut
- PMID: 27383983
- PMCID: PMC5114849
- DOI: 10.1038/nature18849
Interactions between the microbiota and pathogenic bacteria in the gut
Abstract
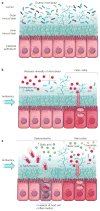
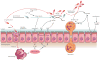
The microbiome has an important role in human health. Changes in the microbiota can confer resistance to or promote infection by pathogenic bacteria. Antibiotics have a profound impact on the microbiota that alters the nutritional landscape of the gut and can lead to the expansion of pathogenic populations. Pathogenic bacteria exploit microbiota-derived sources of carbon and nitrogen as nutrients and regulatory signals to promote their own growth and virulence. By eliciting inflammation, these bacteria alter the intestinal environment and use unique systems for respiration and metal acquisition to drive their expansion. Unravelling the interactions between the microbiota, the host and pathogenic bacteria will produce strategies for manipulating the microbiota against infectious diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
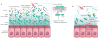
References
-
- Ley RE, Peterson DA, Gordon JI. Ecological and evolutionary forces shaping microbial diversity in the human intestine. Cell. 2006;124:837–848. - PubMed
-
- Yurist-Doutsch S, Arrieta MC, Vogt SL, Finlay BB. Gastrointestinal microbiota-mediated control of enteric pathogens. Annu Rev Genet. 2014;48:361–382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI114511/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI053067/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI077613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI096528/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI105135/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI053067/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI114922/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI114511/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI077613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI117940/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI112445/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI114922/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI044170/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI05135/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI112445/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI096528/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI053067/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI044170/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI117940/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

