Current status and perspectives of Clonorchis sinensis and clonorchiasis: epidemiology, pathogenesis, omics, prevention and control
- PMID: 27384714
- PMCID: PMC4933995
- DOI: 10.1186/s40249-016-0166-1
Current status and perspectives of Clonorchis sinensis and clonorchiasis: epidemiology, pathogenesis, omics, prevention and control
Abstract
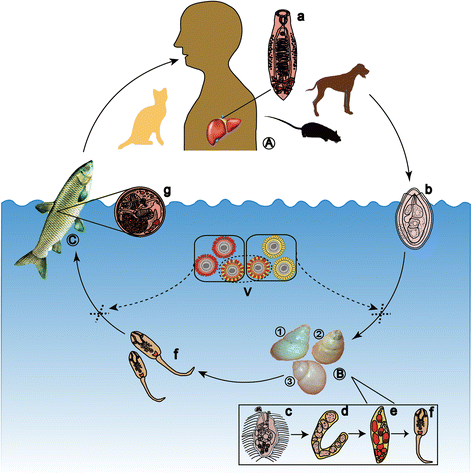
Clonorchiasis, caused by Clonorchis sinensis (C. sinensis), is an important food-borne parasitic disease and one of the most common zoonoses. Currently, it is estimated that more than 200 million people are at risk of C. sinensis infection, and over 15 million are infected worldwide. C. sinensis infection is closely related to cholangiocarcinoma (CCA), fibrosis and other human hepatobiliary diseases; thus, clonorchiasis is a serious public health problem in endemic areas. This article reviews the current knowledge regarding the epidemiology, disease burden and treatment of clonorchiasis as well as summarizes the techniques for detecting C. sinensis infection in humans and intermediate hosts and vaccine development against clonorchiasis. Newer data regarding the pathogenesis of clonorchiasis and the genome, transcriptome and secretome of C. sinensis are collected, thus providing perspectives for future studies. These advances in research will aid the development of innovative strategies for the prevention and control of clonorchiasis.
Keywords: Clonorchiasis; Clonorchis sinensis; Diagnosis; Omics; Pathogenesis; Prevention.
Figures
References
-
- Chung PR, Soh CT. Snail-borne parasitic zoonoses in Korea. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1991;22(Suppl):391–5. - PubMed
-
- Choi DW. Clonorchis sinensis: life cycle, intermediate hosts, transmission to man and geographical distribution in Korea. Arzneimittelforschung. 1984;34(9B):1145–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

