Association of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2 Alpha Gene Polymorphisms with the Risk of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Liver Disease in Guangxi Chinese: A Case-Control Study
- PMID: 27384772
- PMCID: PMC4934873
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158241
Association of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2 Alpha Gene Polymorphisms with the Risk of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Liver Disease in Guangxi Chinese: A Case-Control Study
Abstract
Objective: Hypoxia-inducible factor-2 alpha (HIF-2a) plays a major role in the progression of disease, although the role of HIF-2α gene polymorphisms in hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related diseases remains elusive. The aim of this study is to determine whether HIF-2a rs13419896 and rs6715787 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are associated with susceptibility to chronic hepatitis B (CHB), liver cirrhosis (LC), or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
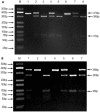
Method: A case-control study of 107 patients with CHB, 83 patients with LC, 234 patients with HCC, and 224 healthy control subjects was carried out, and the HIF-2a rs13419896 and rs6715787 SNPs were genotyped by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP).
Results: No significant differences were observed in the genotype or allele frequency of two HIF-2a SNPs between the cases and controls (all p>0.05). However, in subgroup analysis by gender, the HIF-2a rs13419896 GA and AA genotypes were significantly associated with a risk of CHB (odds ratio [OR] = 3.565, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.123-11.314, p = 0.031 and OR = 12.506, 95% CI = 1.329-117.716, p = 0.027) in females, and the A allele of rs13419896 was associated with a risk of CHB (OR = 2.624, 95% CI = 1.244-5.537, p = 0.011) and LC (OR = 2.351, 95% CI = 1.002-5.518, p = 0.050) in females. The rs6715787 CG genotype polymorphism may contribute to a reduced risk of LC in the Guangxi Zhuang Chinese population (OR = 0.152, 95% CI = 0.028-0.807, p = 0.027), as determined via subgroup analysis by ethnicity. Moreover, binary logistic regression analyses that were adjusted by drinking status indicated that the AA genotype of rs13419896 may contribute to an increased risk of LC in the non-alcohol-drinking population (OR = 3.124, 95% CI = 1.091-8.947, p = 0.034). In haplotype analysis, GG haplotype was significantly associated with a reduced risk of LC (OR = 0.601, 95% CI = 0.419-0.862, p = 0.005).
Conclusions: The HIF-2a rs13419896 polymorphism is associated with an increased risk of CHB and LC in the Guangxi Chinese population, especially in females and in the non-alcohol-drinking population, while the HIF-2a gene rs6715787 polymorphism is associated with a decreased risk of LC in the Guangxi Zhuang population.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between catalase gene polymorphisms and risk of chronic hepatitis B, hepatitis B virus-related liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in Guangxi population: a case-control study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Apr;94(13):e702. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000702. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 25837767 Free PMC article.
-
Association of PvuII and XbaI polymorphisms in estrogen receptor alpha gene with the risk of hepatitis B virus infection in the Guangxi Zhuang population.Infect Genet Evol. 2014 Oct;27:69-76. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2014.07.002. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Infect Genet Evol. 2014. PMID: 25014269
-
The association between TNFR gene polymorphisms and the risk of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Liver Diseases in Chinese population.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 18;8(1):9240. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27623-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29915336 Free PMC article.
-
Association of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α expression with susceptibility to hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Int J Biol Markers. 2023 Dec;38(3-4):149-158. doi: 10.1177/03936155231204391. Epub 2023 Oct 3. Int J Biol Markers. 2023. PMID: 37787154 Review.
-
The TNF-α rs361525 and IFN-γ rs2430561 polymorphisms are associated with liver cirrhosis risk: a comprehensive meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 14;14:1129767. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1129767. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37122734 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The role of EPAS1 polymorphisms on COPD susceptibility in southern Chinese.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 23;9(10):e20226. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20226. eCollection 2023 Oct. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37876439 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative assessment of HLA-DQ gene polymorphisms with the development of hepatitis B virus infection, clearance, liver cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 5;9(1):96-109. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22941. eCollection 2018 Jan 2. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29416599 Free PMC article.
-
The role of IL22 polymorphisms on liver cirrhosis in patients with hepatitis B virus: A case control study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Nov;98(44):e17867. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017867. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31689880 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen Sensing and Viral Replication: Implications for Tropism and Pathogenesis.Viruses. 2020 Oct 25;12(11):1213. doi: 10.3390/v12111213. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33113858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of Heterozygosity for KrasG12D Promotes Malignant Phenotype of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma by Activating HIF-2α-c-Myc-Regulated Glutamine Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 15;23(12):6697. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126697. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harkisoen S, Arends JE, van Erpecum KJ, van den Hoek A, Hoepelman AI. Hepatitis B viral load and risk of HBV-related liver disease: from East to West? Annals of hepatology. 2012;11(2):164–71. Epub 2012/02/22. . - PubMed
-
- Lofstedt T, Fredlund E, Holmquist-Mengelbier L, Pietras A, Ovenberger M, Poellinger L, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-2alpha in cancer. Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex). 2007;6(8):919–26. Epub 2007/04/04. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

