Polo-like kinase 1 inhibition diminishes acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer with T790M mutations
- PMID: 27384992
- PMCID: PMC5216995
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.10332
Polo-like kinase 1 inhibition diminishes acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer with T790M mutations
Abstract
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are effective against non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with activating EGFR mutations, but resistance is inevitable. Mechanisms of acquired resistance include T790M mutations and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). One potential strategy for overcoming this resistance is the inhibition of polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) based on our previous studies showing that mesenchymal NSCLC cell lines are more sensitive to PLK1 inhibition than epithelial cell lines. To determine the extent to which PLK1 inhibition overcomes EGFR TKI resistance we measured the effects of the PLK1 inhibitor volasertib alone and in combination with the EGFR inhibitor erlotinib in vitro and in vivo in EGFR mutant NSCLC cell lines with acquired resistance to erlotinib. Two erlotinib-resistant cell lines that underwent EMT had higher sensitivity to volasertib, which caused G2/M arrest and apoptosis, than their parental cells. In all NSCLC cell lines with T790M mutations, volasertib markedly reduced erlotinib resistance. All erlotinib-resistant NSCLC cell lines with T790M mutations had higher sensitivity to erlotinib plus volasertib than to erlotinib alone, and the combination treatment caused G2/M arrest and apoptosis. Compared with either agent alone, the combination treatment also caused significantly more DNA damage and greater reductions in tumor size. Our results suggest that PLK1 inhibition is clinically effective against NSCLC that becomes resistant to EGFR inhibition through EMT or the acquisition of a T790M mutation. These results uncover new functions of PLK1 inhibition in the treatment of NSCLC with acquired resistance to EGFR TKIs.
Keywords: drug resistance; epidermal growth factor receptor; epithelial–mesenchymal transition; non-small cell lung cancer; polo-like kinase.
Conflict of interest statement
Research funding from GlaxoSmithKline (J.V. Heymach), Astra Zeneca (J.V. Heymach), and PIQUR Pharmaceuticals (F.M. Johnson). Membership on scientific advisory boards for Astra Zeneca (J.V. Heymach), GlaxoSmithKline (J.V. Heymach), Genentech (J.V. Heymach). All others declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




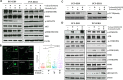
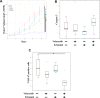
References
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, Palmero R, Garcia-Gomez R, Pallares C, Sanchez JM, Porta R, Cobo M, Garrido P, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:239–246. - PubMed
-
- Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, Sunpaweravong P, Han B, Margono B, Ichinose Y, Nishiwaki Y, Ohe Y, Yang JJ, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:947–957. - PubMed
-
- Sequist LV, Yang JC, Yamamoto N, O'Byrne K, Hirsh V, Mok T, Geater SL, Orlov S, Tsai CM, Boyer M, Su WC, Bennouna J, Kato T, et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3327–3334. - PubMed
-
- Matikas A, Mistriotis D, Georgoulias V, Kotsakis A. Current and Future Approaches in the Management of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients With Resistance to EGFR TKIs. Clin Lung Cancer. 2015;16:252–261. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

