Experiences, perceptions and preferences of mothers towards childhood immunization reminder/recall in Ibadan, Nigeria: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 27386039
- PMCID: PMC4919677
- DOI: 10.11604/pamj.2015.20.243.6019
Experiences, perceptions and preferences of mothers towards childhood immunization reminder/recall in Ibadan, Nigeria: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Introduction: Immunization reminder/recall system is proven as one of the effective ways of improving immunization rates. Prior to the development and implementation of an immunization reminder/recall system intervention, we explored the experiences, preferences and perceptions towards childhood immunization reminder/recall among 614 mothers of infants in Ibadan, Nigeria.
Methods: A cross-sectional health facility-based survey utilizing a semi-structured questionnaire was conducted in four Primary Health Care centers. Descriptive statistics were computed using SPSS. Logistic models were used to investigate the relationships with specific outcomes.
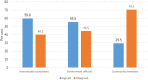
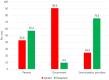
Results: Only 3.9% had ever heard of immunization reminder/recall and 1.5% had ever received one. However, 97.9% were willing to record their cellphone numbers in the clinics for immunization reminder/recall and 95.1% were willing to receive. Their preferred communication modes were cell phone calls (57.6%) or text messages/SMS (35.6%). Only 2.2% preferred home-visits and 0.4%, e-mails. About 4% were not willing to receive any form of immunization reminder/recall. Mothers with post-secondary education were more likely to prefer SMS than other mothers (OR 2.3, 95% CI 1.7-3.3, p.
Conclusion: This study provided critical baseline data for designing a reminder/recall intervention for routine childhood immunization in the study communities. The findings may serve as a guide for public health professionals in designing reminder/recall strategies to improve childhood immunization.
Keywords: Mothers; childhood; community; experiences; immunization; preferences; reminder/recall.
Figures
References
-
- WHO, UNICEF. World Bank State of the World's Vaccines and Immunization. 3rd ed. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2009. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2009/9789241563864_eng.pdf. Accessed January 14, 2011.
-
- National Primary Health Care Development Agency (NPHCDA) 2010. Report on 2010 National immunization coverage survey. Abuja, Nigeria: NPHCDA; 2010.
-
- World Health Organization. Immunization, surveillance, assessment and monitoring; Vaccine preventable disease; http//www.who.int/immunization/monitoring/en. Accessed May 22, 2012.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Global routine vaccination coverage, 2010. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2011;60(44):1520–2. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Nigeria launches penta vaccine; http://www.afro.who.int/en/nigeria/press-materials/item/4735-nigeria-lau.... Accessed October 14, 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical