Process optimization for green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum MTCC 8785 and evaluation of its antibacterial properties
- PMID: 27386310
- PMCID: PMC4920743
- DOI: 10.1186/s40064-016-2558-x
Process optimization for green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum MTCC 8785 and evaluation of its antibacterial properties
Abstract
Background: Eco-friendly synthesis of nanoparticles is viewed as an alternative to the chemical method and initiated the use of microorganisms for synthesis. The present study has been designed to utilize plant pathogenic fungi Sclerotinia sclerotiorum MTCC 8785 strain for synthesis and optimization of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) production as well as evaluation of antibacterial properties. The AgNPs were synthesized by reduction of aqueous silver nitrate (AgNO3) solution after incubation of 3-5 days at room temperature. The AgNPs were further characterized using UV-visible spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Reaction parameters including media, fungal biomass, AgNO3 concentration, pH and temperature were further optimized for rapid AgNPs production. The antibacterial efficacy of AgNPs was evaluated against Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 by disc diffusion and growth kinetics assay at the concentration determined by the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC).
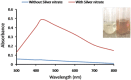
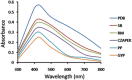
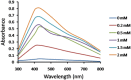
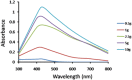
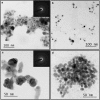
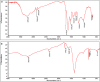
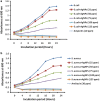
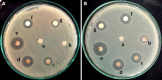
Results: AgNPs synthesis was initially marked by the change in colour from pale white to brown and was confirmed by UV-Vis spectroscopy. Optimization studies showed that potato dextrose broth (PDB) media, 10 g of biomass, addition of 2 mM AgNO3, pH 11 and 80 °C temperature resulted in enhanced AgNPs synthesis through extracellular route. TEM data revealed spherical shape AgNPs with size in the range of 10 nm. Presence of proteins capped to AgNPs was confirmed by FTIR. AgNPs showed antibacterial activity against E. coli and S. aureus at 100 ppm concentration, corresponding MIC value.
Conclusion: S. sclerotiorum MTCC 8785 mediated AgNPs was synthesized rapidly under optimized conditions, which showed antibacterial activity.
Keywords: Antibacterial activity; Green synthesis; Optimization; Sclerotinia sclerotiorum; Silver nanoparticles.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum MTCC 8785 as a biological agent for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles and assessment of their antifungal potential against Trichoderma harzianum MTCC 801.Environ Res. 2023 Jan 1;216(Pt 3):114752. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.114752. Epub 2022 Nov 6. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 36351471
-
Efficient visible light induced synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Penicillium polonicum ARA 10 isolated from Chetomorpha antennina and its antibacterial efficacy against Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2018 Mar;180:175-185. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.02.005. Epub 2018 Feb 7. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2018. PMID: 29453129
-
Biogenic nanosilver bearing antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities and its potential for application in agriculture and industry.Front Microbiol. 2023 Feb 20;14:1125685. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1125685. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36891391 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Mediated by Fungi: A Review.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019 Oct 22;7:287. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00287. eCollection 2019. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31696113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bell Shape Curves of Hemolysis Induced by Silver Nanoparticles: Review and Experimental Assay.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Mar 24;12(7):1066. doi: 10.3390/nano12071066. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35407184 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Statistical optimization of experimental parameters for extracellular synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by a novel haloalaliphilic Alkalibacillus sp.W7.Sci Rep. 2021 May 25;11(1):10924. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90408-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34035407 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by Talaromyces funiculosus for therapeutic applications and safety evaluation.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 21;15(1):13750. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95899-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40258887 Free PMC article.
-
Multifarious global flora fabricated phytosynthesis of silver nanoparticles: a green nanoweapon for antiviral approach including SARS-CoV-2.Int Nano Lett. 2022;12(4):313-344. doi: 10.1007/s40089-022-00367-z. Epub 2022 Feb 12. Int Nano Lett. 2022. PMID: 35194512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological Synthesis of Monodisperse Uniform-Size Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) by Fungal Cell-Free Extracts at Elevated Temperature and pH.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Apr 23;8(5):439. doi: 10.3390/jof8050439. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35628695 Free PMC article.
-
Improved biosynthesis and characteristics of silver nanoparticles using marine endophytic fungi exposed to hypo-osmotic stress.Sci Rep. 2025 May 10;15(1):16327. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-98978-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40348898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad A, Mukherjee P, Senapati S, Mandal D, Khan MI, Kumar R, Sastry M. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Fusarium oxysporum. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2003;28:313–318. doi: 10.1016/S0927-7765(02)00174-1. - DOI
-
- Albrecht M, Evans C, Raston C. Green chemistry and the health implications of nanoparticles. Green Chem. 2006;8:417. doi: 10.1039/b517131h. - DOI
-
- Banu A, Rathod V, Ranganath E. Silver nanoparticle production by Rhizopus stolonifer and its antibacterial activity against extended spectrum β-lactamase producing (ESBL) strains of Enterobacteriaceae. Mater Res Bull. 2011;46:1417–1423. doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2011.05.008. - DOI
-
- Basavaraja S, Balaji S, Lagashetty A, Rajasab A, Venkataraman A. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Fusarium semitectum. Mater Res Bull. 2008;43:1164–1170. doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2007.06.020. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

