Elevated d-dimer cut-off values for computed tomography pulmonary angiography-d-dimer correlates with location of embolism
- PMID: 27386486
- PMCID: PMC4916352
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2016.05.55
Elevated d-dimer cut-off values for computed tomography pulmonary angiography-d-dimer correlates with location of embolism
Abstract
Background: Acute pulmonary embolism (APE) is a potentially fatal condition, and making a timely diagnosis can be challenging. Computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) has become the modality of choice, and this contributes to the increasing load on emergency room CT scanners. Our purpose was to investigate whether an elevated d-dimer cut-off could reduce the demand for CTPA while maintaining a high sensitivity and negative predictive value (NPV).
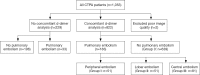
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed all patients referred for CTPA with suspicion of APE in 2012, and collected d-dimer values and CTPA results. We investigated the diagnostic performance of d-dimer using a 0.5 mg/L cut-off and an age adjusted cut-off. We also evaluated a new and elevated cut-off. Cases were categorized according to their CTPA result into: no embolism, peripheral embolism, lobar embolism and central embolism. Finally we investigated a possible correlation between d-dimer values and location of embolism.
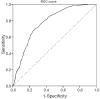
Results: We included 1,051 CTPAs, from which 216 (21%) showed pulmonary embolism. There were concomitant d-dimer analyses in 822 CTPA examinations. The current 0.5 mg/L cut-off achieved a sensitivity and NPV of 99%. The age-adjusted cut-off achieved a sensitivity and NPV of 98%, and our suggested cut-off of 0.9 mg/L achieved a sensitivity and NPV of 97%.
Conclusions: We conclude that the elevated d-dimer cut-off of 0.9 mg/L achieved a high sensitivity and NPV, while reducing the number of CTPA by 27%. The correlation between d-dimer values and location of embolisms supports the suggestion of an elevated d-dimer value.
Keywords: Computed tomography; pulmonary embolism; sensitivity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Precision in Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosis: Leveraging D-dimer Levels With Computed Tomography Pulmonary Angiography (CTPA) Insights.Cureus. 2024 Aug 25;16(8):e67765. doi: 10.7759/cureus.67765. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39328639 Free PMC article.
-
[Diagnostic value of D-dimer combined with Wells score for suspected pulmonary embolism].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018 Oct 18;50(5):828-832. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018. PMID: 30337743 Chinese.
-
Exclusion of acute pulmonary embolism: computed tomography pulmonary angiogram or D-dimer?Singapore Med J. 2009 Apr;50(4):403-6. Singapore Med J. 2009. PMID: 19421686
-
A critical appraisal of non-invasive diagnosis and exclusion of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in outpatients with suspected deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism: how many tests do we need?Int Angiol. 2005 Mar;24(1):27-39. Int Angiol. 2005. PMID: 15876996 Review.
-
Computed tomography pulmonary angiography as a single imaging test to rule out pulmonary embolism.Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2011 Sep;17(5):380-6. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0b013e328348b3de. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2011. PMID: 21681098 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Multiple D-Dimer Cutoff Thresholds and Other Clinically Applicable Biomarkers for the Detection and Radiographic Evaluation of Pulmonary Embolism.Adv Respir Med. 2022 Aug 5;90(4):300-309. doi: 10.3390/arm90040039. Adv Respir Med. 2022. PMID: 36004959 Free PMC article.
-
Precision in Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosis: Leveraging D-dimer Levels With Computed Tomography Pulmonary Angiography (CTPA) Insights.Cureus. 2024 Aug 25;16(8):e67765. doi: 10.7759/cureus.67765. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39328639 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic approach and use of CTPA in patients with suspected pulmonary embolism in an emergency department in Saudi Arabia.Blood Res. 2023 Mar 31;58(1):51-60. doi: 10.5045/br.2023.2023007. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Blood Res. 2023. PMID: 36922446 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Ability of Open-Source Artificial Intelligence to Predict Accepting-Journal Impact Factor and Eigenfactor Score Using Academic Article Abstracts: Cross-sectional Machine Learning Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Mar 7;25:e42789. doi: 10.2196/42789. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 36881455 Free PMC article.
-
The Correlation Between the D-Dimer Values and Anatomical Distribution of Pulmonary Embolism.Med Arch. 2023;77(5):354-357. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2023.77.354-357. Med Arch. 2023. PMID: 38299089 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cohen AT, Agnelli G, Anderson FA, et al. Venous thromboembolism (VTE) in Europe. The number of VTE events and associated morbidity and mortality. Thromb Haemost 2007;98:756-64. - PubMed
-
- Oger E. Incidence of venous thromboembolism: a community-based study in Western France. EPI-GETBP Study Group. Groupe d'Etude de la Thrombose de Bretagne Occidentale. Thromb Haemost 2000;83:657-60. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
