Rituximab in refractory myasthenia gravis: a prospective, open-label study with long-term follow-up
- PMID: 27386504
- PMCID: PMC4931720
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.314
Rituximab in refractory myasthenia gravis: a prospective, open-label study with long-term follow-up
Abstract
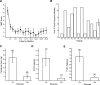
We examined the clinical effectiveness of rituximab in fourteen patients with refractory myasthenia gravis (MG). Manual muscle testing (MMT) score was recorded at baseline and followed during the course of the study. Steroid dose, frequency of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) infusions, and plasma exchange (PLEX) were also monitored throughout the duration of the study. All patients responded dramatically to rituximab, as measured by a change in MMT score, prednisone dose, or the frequency of IVIG infusions or PLEX. Rituximab appears safe and effective for the treatment of refractory MG. It should be considered as a therapeutic option in refractory patients.
Figures
References
-
- Gilhus NE, Verschuuren JJ. Myasthenia gravis: subgroup classification and therapeutic strategies. Lancet Neurol 2015;14:1023–1036. - PubMed
-
- Boye J, Elter T, Engert A. An overview of the current clinical use of the anti‐CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab. Ann Oncol 2003;14:520–535. - PubMed
-
- Stieglbauer K, Topakian R, Schaffer V, Aichner FT. Rituximab for myasthenia gravis: three case reports and review of the literature. J Neurol Sci 2009;280:120–122. - PubMed
-
- Zebardast N, Patwa HS, Novella SP, Goldstein JM. Rituximab in the management of refractory myasthenia gravis. Muscle Nerve 2010;41:375–378. - PubMed
-
- Collongues N, Casez O, Lacour A, et al. Rituximab in refractory and non‐refractory myasthenia: a retrospective multicenter study. Muscle Nerve 2012;46:687–691. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

