Dopamine D1 signaling organizes network dynamics underlying working memory
- PMID: 27386561
- PMCID: PMC4928887
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.1501672
Dopamine D1 signaling organizes network dynamics underlying working memory
Abstract
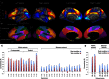
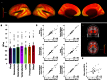
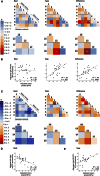
Local prefrontal dopamine signaling supports working memory by tuning pyramidal neurons to task-relevant stimuli. Enabled by simultaneous positron emission tomography-magnetic resonance imaging (PET-MRI), we determined whether neuromodulatory effects of dopamine scale to the level of cortical networks and coordinate their interplay during working memory. Among network territories, mean cortical D1 receptor densities differed substantially but were strongly interrelated, suggesting cross-network regulation. Indeed, mean cortical D1 density predicted working memory-emergent decoupling of the frontoparietal and default networks, which respectively manage task-related and internal stimuli. In contrast, striatal D1 predicted opposing effects within these two networks but no between-network effects. These findings specifically link cortical dopamine signaling to network crosstalk that redirects cognitive resources to working memory, echoing neuromodulatory effects of D1 signaling on the level of cortical microcircuits.
Keywords: Neuroscience; dopamine; working memory.
Figures
References
-
- Sawaguchi T., Goldman-Rakic P. S., D1 dopamine receptors in prefrontal cortex: Involvement in working memory. Science 251, 947–950 (1991). - PubMed
-
- Williams G. V., Goldman-Rakic P. S., Modulation of memory fields by dopamine D1 receptors in prefrontal cortex. Nature 376, 572–575 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Gamo N. J., Lur G., Higley M. J., Wang M., Paspalas C. D., Vijayraghavan S., Yang Y., Ramos B. P., Peng K., Kata A., Boven L., Lin F., Roman L., Lee D., Arnsten A. F. T., Stress impairs prefrontal cortical function via D1 dopamine receptor interactions with hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. Biol. Psychiatry 78, 860–870 (2015). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- S10 RR017208/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR026666/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB018964/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB014894/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR022976/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH084059/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101425/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR023385/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR019933/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB015896/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS083534/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR023401/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

