Early-life nutrition modulates the epigenetic state of specific rDNA genetic variants in mice
- PMID: 27386920
- PMCID: PMC5734613
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aaf7040
Early-life nutrition modulates the epigenetic state of specific rDNA genetic variants in mice
Abstract
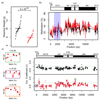
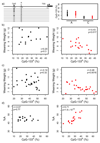
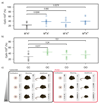
A suboptimal early-life environment, due to poor nutrition or stress during pregnancy, can influence lifelong phenotypes in the progeny. Epigenetic factors are thought to be key mediators of these effects. We show that protein restriction in mice from conception until weaning induces a linear correlation between growth restriction and DNA methylation at ribosomal DNA (rDNA). This epigenetic response remains into adulthood and is restricted to rDNA copies associated with a specific genetic variant within the promoter. Related effects are also found in models of maternal high-fat or obesogenic diets. Our work identifies environmentally induced epigenetic dynamics that are dependent on underlying genetic variation and establishes rDNA as a genomic target of nutritional insults.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no conflict of interest
Figures

References
-
- Radford EJ, Ito M, Shi H, Corish JA, Yamazawa K, Isganaitis E, Seisenberger S, Hore TA, Reik W, Erkek S, Peters AH, et al. In utero effects. In utero undernourishment perturbs the adult sperm methylome and intergenerational metabolism. Science. 2014;345 doi: 10.1126/science.1255903. 1255903; published online EpubAug 15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MC_UU_12012/4/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/G00711/X/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/M012494/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/G00711X/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- FS/12/64/30001/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

