Connexins and their channels in inflammation
- PMID: 27387655
- PMCID: PMC5584657
- DOI: 10.1080/10409238.2016.1204980
Connexins and their channels in inflammation
Abstract
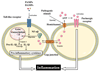
Inflammation may be caused by a variety of factors and is a hallmark of a plethora of acute and chronic diseases. The purpose of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cell injury trigger, to clear out dead cells from damaged tissue and to initiate tissue regeneration. Despite the wealth of knowledge regarding the involvement of cellular communication in inflammation, studies on the role of connexin-based channels in this process have only begun to emerge in the last few years. In this paper, a state-of-the-art overview of the effects of inflammation on connexin signaling is provided. Vice versa, the involvement of connexins and their channels in inflammation will be discussed by relying on studies that use a variety of experimental tools, such as genetically modified animals, small interfering RNA and connexin-based channel blockers. A better understanding of the importance of connexin signaling in inflammation may open up towards clinical perspectives.
Keywords: Connexins; cytokines; gap junctions; hemichannels; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Coordination of innate immune responses by connexins.Front Immunol. 2025 May 22;16:1594015. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1594015. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40475783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gap junctions and connexin-mediated communication in the immune system.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Mar 23;1662(1-2):102-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2003.10.021. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15033582 Review.
-
Emerging issues of connexin channels: biophysics fills the gap.Q Rev Biophys. 2001 Aug;34(3):325-472. doi: 10.1017/s0033583501003705. Q Rev Biophys. 2001. PMID: 11838236 Review.
-
Gap junctions and connexins: potential contributors to the immunological synapse.J Leukoc Biol. 2002 Oct;72(4):636-42. J Leukoc Biol. 2002. PMID: 12377931 Review.
-
Connexins participate in the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis.Semin Immunopathol. 2009 Jun;31(1):49-61. doi: 10.1007/s00281-009-0147-6. Epub 2009 Apr 30. Semin Immunopathol. 2009. PMID: 19404645 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of Connexins 37, 40 and 45, Pannexin 1 and Vimentin in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas.Genes (Basel). 2023 Feb 9;14(2):446. doi: 10.3390/genes14020446. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36833374 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium probiotic cocktail on modulation of gene expression of gap junctions dysregulated by intestinal pathogens.Arch Microbiol. 2022 Jun 23;204(7):417. doi: 10.1007/s00203-022-03026-1. Arch Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35737111
-
Cardiolipotoxicity, Inflammation, and Arrhythmias: Role for Interleukin-6 Molecular Mechanisms.Front Physiol. 2019 Jan 7;9:1866. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01866. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30666212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Connexin 43: A Target for the Treatment of Inflammation in Secondary Complications of the Kidney and Eye in Diabetes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 6;23(2):600. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020600. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Connexin-43 in the Inflammatory Process: A New Potential Therapy to Influence Keratitis.J Ophthalmol. 2019 Jan 21;2019:9312827. doi: 10.1155/2019/9312827. eCollection 2019. J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 30805212 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abed A, Dussaule JC, Boffa JJ, Chatziantoniou C, Chadjichristos CE. Connexins in renal endothelial function and dysfunction. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2014a;14:15–21. - PubMed
-
- Abed A, Toubas J, Kavvadas P, Authier F, Cathelin D, Alfieri C, Boffa JJ, Dussaule JC, Chatziantoniou C, Chadjichristos CE. Targeting connexin 43 protects against the progression of experimental chronic kidney disease in mice. Kidney Int. 2014b;86:768–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
