Eribulin-induced liver dysfunction as a prognostic indicator of survival of metastatic breast cancer patients: a retrospective study
- PMID: 27389013
- PMCID: PMC4936231
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-016-2436-5
Eribulin-induced liver dysfunction as a prognostic indicator of survival of metastatic breast cancer patients: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Eribulin is a non-taxane, microtubule dynamics inhibitor that increases survival of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Although eribulin is well tolerated in patients with heavily pretreated disease, eribulin-induced liver dysfunction (EILD) can occur, resulting in treatment modification and subsequent poor disease control. We aimed to clarify the effect of EILD on patient survival.
Methods: The medical records of 157 metastatic breast cancer patients treated with eribulin between July 2011 and November 2013 at Cancer Institute Hospital were retrospectively analyzed. EILD was defined as 1) an increase in alanine aminotransferase or aspartate aminotransferase levels >3 times the upper limit of normal, and/or 2) initiation of a liver-supporting oral drug therapy such as ursodeoxycholic acid or glycyron. Fatty liver was defined as a decrease in the liver-to-spleen attenuation ratio to <0.9 on a computed tomography scan.
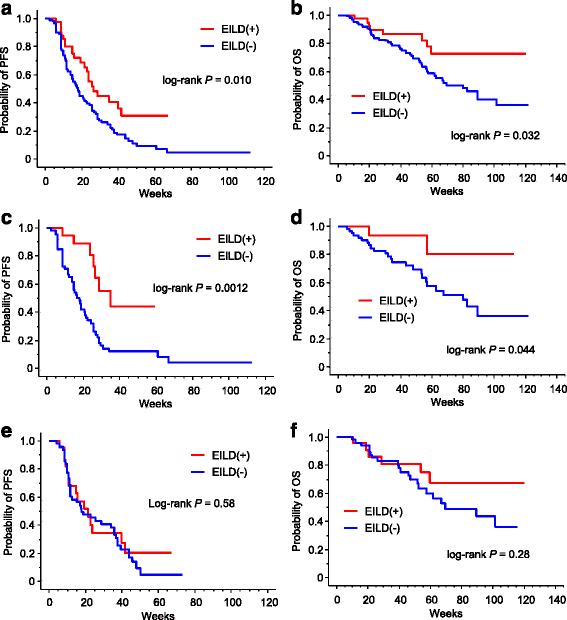
Results: EILD occurred in 42 patients, including one patient for whom eribulin treatment was discontinued due to severe EILD. The patients who developed EILD had significantly higher body mass indices (BMIs) than those who did not develop EILD (24.5 vs. 21.5, respectively; P < 0.0001), with no difference in the dose intensity of eribulin between the two groups (P = 0.76). Interestingly, the patients with EILD exhibited significantly longer progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) than those without EILD (P = 0.010 and P = 0.032, respectively). Similarly, among 80 patients without liver metastasis, 19 with EILD exhibited significantly longer PFS and OS than the others (P = 0.0012 and P = 0.044, respectively), and EILD was an independent prognostic factor of PFS (P = 0.0079) in multivariate analysis. During eribulin treatment, 18 patients developed fatty liver, 11 of whom developed EILD, with a median BMI of 26.7.
Conclusions: Although EILD and fatty liver occurred at a relatively high frequency in our study, most of the patients did not experience severe adverse effects. Surprisingly, the development of EILD was positively associated with patient survival, especially in patients without liver metastases. EILD may be a clinically useful predictive biomarker of survival, but further studies are needed to confirm these findings in another cohort of patients.
Keywords: Eribulin-induced liver dysfunction; Fatty liver disease; Metastatic breast cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phase II clinical study of eribulin monotherapy in Japanese patients with metastatic breast cancer who had well-defined taxane resistance.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Jun;157(2):295-305. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-3808-x. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 27125669 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of eribulin monotherapy in patients with heavily pretreated metastatic breast cancer.J BUON. 2016 Mar-Apr;21(2):375-81. J BUON. 2016. PMID: 27273947
-
Eribulin efficacy based on type of metastatic site: a real-life study in heavily pretreated metastatic breast cancer.Future Oncol. 2017 Apr;13(11s):5-10. doi: 10.2217/fon-2017-0017. Future Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28481186
-
Advances in therapy: eribulin improves survival for metastatic breast cancer.Anticancer Drugs. 2010 Nov;21(10):885-9. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e32833ed62e. Anticancer Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20838209 Review.
-
The safety of eribulin for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2019 May;18(5):347-355. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2019.1608946. Epub 2019 May 20. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2019. PMID: 31107111 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship between Chewing Status and Fatty Liver Diagnosed by Liver/Spleen Attenuation Ratio: A Cross-Sectional Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 25;20(1):307. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010307. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36612629 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of renal function on neutrophil decreases following eribulin administration.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2020 Oct;3(5):e1258. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1258. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 33085846 Free PMC article.
-
Postdiagnosis body fatness, weight change and breast cancer prognosis: Global Cancer Update Program (CUP global) systematic literature review and meta-analysis.Int J Cancer. 2023 Feb 15;152(4):572-599. doi: 10.1002/ijc.34322. Epub 2022 Oct 24. Int J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36279884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cortes J, O’Shaughnessy J, Loesch D, Blum JL, Vahdat LT, Petrakova K, Chollet P, Manikas A, Dieras V, Delozier T, et al. Eribulin monotherapy versus treatment of physician’s choice in patients with metastatic breast cancer (EMBRACE): a phase 3 open-label randomised study. Lancet. 2011;377(9769):914–23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60070-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vahdat LT, Pruitt B, Fabian CJ, Rivera RR, Smith DA, Tan-Chiu E, Wright J, Tan AR, Dacosta NA, Chuang E, et al. Phase II study of eribulin mesylate, a halichondrin B analog, in patients with metastatic breast cancer previously treated with an anthracycline and a taxane. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(18):2954–61. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.17.7618. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cortes J, Vahdat L, Blum JL, Twelves C, Campone M, Roche H, Bachelot T, Awada A, Paridaens R, Goncalves A, et al. Phase II study of the halichondrin B analog eribulin mesylate in patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer previously treated with an anthracycline, a taxane, and capecitabine. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(25):3922–8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.25.8467. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

