From suspected Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease to confirmed histoplasma meningitis
- PMID: 27389723
- PMCID: PMC4956983
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2016-214937
From suspected Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease to confirmed histoplasma meningitis
Abstract
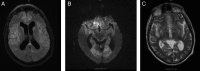
A 77-year-old man with chronic obstructive lung disease who was on steroids, presented to the hospital after a fall with subacute headaches and ataxia. During the patient's hospital course, his clinical condition deteriorated with myoclonic jerks, fevers and severe encephalopathy. An extensive workup, including EEG, brain MRI and lumbar puncture, revealed possible Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Unfortunately, the patient failed to improve and died 12 days after admission. A brain-only autopsy revealed he had acute histoplasma meningitis with patchy superficial cerebritis.
2016 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Isolated central nervous system histoplasmosis presenting with ischemic pontine stroke and meningitis in an immune-competent patient.JAMA Neurol. 2013 May;70(5):638-41. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.1043. JAMA Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23479115
-
Transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease via a corneal transplant.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1997 Sep;63(3):388-90. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.63.3.388. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1997. PMID: 9328261 Free PMC article.
-
Creutzfeldt-Jakob-Like Syndrome due to Hypercalcemic Encephalopathy.Clin EEG Neurosci. 2015 Oct;46(4):327-30. doi: 10.1177/1550059414529764. Epub 2014 Jun 27. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 24973231
-
Coexistence of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, Lewy body disease, and Alzheimer's disease pathology: an autopsy case showing typical clinical features of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.Neuropathology. 2009 Aug;29(4):454-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2008.00964.x. Neuropathology. 2009. PMID: 18715272 Review.
-
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: report of four cases and review of the literature.Turk Patoloji Derg. 2015;31(2):148-52. doi: 10.5146/tjpath.2013.01195. Turk Patoloji Derg. 2015. PMID: 24272930 Review.
Cited by
-
Central nervous system histoplasmosis: Multicenter retrospective study on clinical features, diagnostic approach and outcome of treatment.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Mar;97(13):e0245. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010245. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29595679 Free PMC article.
-
Central Nervous System Infection with Histoplasma capsulatum.J Fungi (Basel). 2019 Jul 24;5(3):70. doi: 10.3390/jof5030070. J Fungi (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31344869 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lin Blache J, Ryan K, Arceneaux K. Histoplasmosis. Compend Contin Educ Vet 2011;33:E1–10; quiz E11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
