Catheter ablation in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 27389907
- PMCID: PMC5353871
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw260
Catheter ablation in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation
Abstract
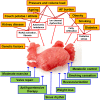
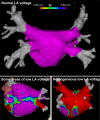
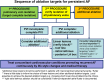
Catheter ablation is increasingly offered to patients who suffer from symptoms due to atrial fibrillation (AF), based on a growing body of evidence illustrating its efficacy compared with antiarrhythmic drug therapy. Approximately one-third of AF ablation procedures are currently performed in patients with persistent or long-standing persistent AF. Here, we review the available information to guide catheter ablation in these more chronic forms of AF. We identify the following principles: Our clinical ability to discriminate paroxysmal and persistent AF is limited. Pulmonary vein isolation is a reasonable and effective first approach for catheter ablation of persistent AF. Other ablation strategies are being developed and need to be properly evaluated in controlled, multicentre trials. Treatment of concomitant conditions promoting recurrent AF by life style interventions and medical therapy should be a routine adjunct to catheter ablation of persistent AF. Early rhythm control therapy has a biological rationale and trials evaluating its value are underway. There is a clear need to generate more evidence for the best approach to ablation of persistent AF beyond pulmonary vein isolation in the form of adequately powered controlled multi-centre trials.
Keywords: Antiarrhythmic drugs; Atrial fibrillation; Catheter ablation; Clinical practice; Complications; Exercise; Indications; Long-standing persistent; Outcomes; Persistent; Rhythm control therapy; Sinus rhythm; Technique; Upstream therapy; Weight loss.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures

References
-
- Chugh SS, Havmoeller R, Narayanan K, Singh D, Rienstra M, Benjamin EJ, Gillum RF, Kim YH, McAnulty JH Jr, Zheng ZJ, Forouzanfar MH, Naghavi M, Mensah GA, Ezzati M, Murray CJ. Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: a Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study. Circulation 2014;129:837–847. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kirchhof P, Ammentorp B, Darius H, De Caterina R, Le Heuzey JY, Schilling RJ, Schmitt J, Zamorano JL. Management of atrial fibrillation in seven European countries after the publication of the 2010 ESC Guidelines on atrial fibrillation: primary results of the PREvention oF thromboemolic events—European Registry in Atrial Fibrillation (PREFER in AF). Europace 2014;16:6–14. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lip GY, Laroche C, Ioachim PM, Rasmussen LH, Vitali-Serdoz L, Petrescu L, Darabantiu D, Crijns HJ, Kirchhof P, Vardas P, Tavazzi L, Maggioni AP, Boriani G. Prognosis and treatment of atrial fibrillation patients by European cardiologists: one year follow-up of the EURObservational Research Programme-Atrial Fibrillation General Registry Pilot Phase (EORP-AF Pilot registry). Eur Heart J 2014;35:3365–3376. - PubMed
-
- Arbelo E, Brugada J, Hindricks G, Maggioni AP, Tavazzi L, Vardas P, Laroche C, Anselme F, Inama G, Jais P, Kalarus Z, Kautzner J, Lewalter T, Mairesse GH, Perez-Villacastin J, Riahi S, Taborsky M, Theodorakis G, Trines SA, Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Pilot Study Investigators. The atrial fibrillation ablation pilot study: a European Survey on Methodology and results of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation conducted by the European Heart Rhythm Association. Eur Heart J 2014;35:1466–1478. - PubMed
-
- Camm AJ, Lip GY, De Caterina R, Savelieva I, Atar D, Hohnloser SH, Hindricks G, Kirchhof P. 2012 focused update of the ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: an update of the 2010 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation—developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association. Europace 2012;14:1385–1413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

