Toward a More Efficient Implementation of Antifibrillation Pacing
- PMID: 27391010
- PMCID: PMC4938213
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158239
Toward a More Efficient Implementation of Antifibrillation Pacing
Abstract
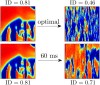
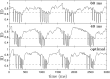
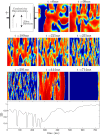
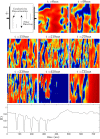
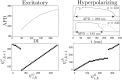
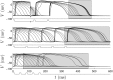
We devise a methodology to determine an optimal pattern of inputs to synchronize firing patterns of cardiac cells which only requires the ability to measure action potential durations in individual cells. In numerical bidomain simulations, the resulting synchronizing inputs are shown to terminate spiral waves with a higher probability than comparable inputs that do not synchronize the cells as strongly. These results suggest that designing stimuli which promote synchronization in cardiac tissue could improve the success rate of defibrillation, and point towards novel strategies for optimizing antifibrillation pacing.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
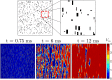
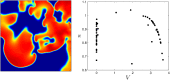
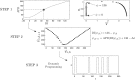
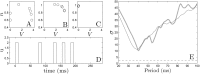
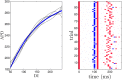
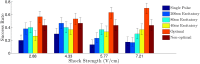
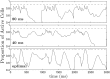
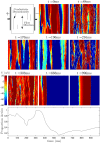
References
-
- Jacq F, Foulldrin G, Savouré A, Anselme F, Baguelin-Pinaud A, Cribier A, et al. A comparison of anxiety, depression and quality of life between device shock and nonshock groups in implantable cardioverter defibrillator recipients. General Hospital Psychiatry. 2009;31(3):266–273. 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2009.01.003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Suzuki T, Shiga T, Kuwahara K, Kobayashi S, Suzuki S, Nishimura K, et al. Prevalence and Persistence of Depression in Patients with Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator: A 2-year Longitudinal Study. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology. 2010;33(12):1455–1461. 10.1111/j.1540-8159.2010.02887.x - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

