Neuroimaging correlates of language network impairment and reorganization in temporal lobe epilepsy
- PMID: 27393391
- PMCID: PMC5215985
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bandl.2016.06.002
Neuroimaging correlates of language network impairment and reorganization in temporal lobe epilepsy
Abstract
Advanced, noninvasive imaging has revolutionized our understanding of language networks in the brain and is reshaping our approach to the presurgical evaluation of patients with epilepsy. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has had the greatest impact, unveiling the complexity of language organization and reorganization in patients with epilepsy both pre- and postoperatively, while volumetric MRI and diffusion tensor imaging have led to a greater appreciation of structural and microstructural correlates of language dysfunction in different epilepsy syndromes. In this article, we review recent literature describing how unimodal and multimodal imaging has advanced our knowledge of language networks and their plasticity in epilepsy, with a focus on the most frequently studied epilepsy syndrome in adults, temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE). We also describe how new analytic techniques (i.e., graph theory) are leading to a refined characterization of abnormal brain connectivity, and how subject-specific imaging profiles combined with clinical data may enhance the prediction of both seizure and language outcomes following surgical interventions.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


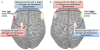
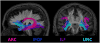
References
-
- Adcock JE, Wise RG, Oxbury JM, Oxbury SM, Matthews PM. Quantitative fMRI assessment of the differences in lateralization of language-related brain activation in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroimage. 2003;18(2):423–438. - PubMed
-
- Albert R, Barabási AL. Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Reviews of modern physics. 2002;74(1):47.
-
- Alessio A, Bonilha L, Rorden C, Kobayashi E, Min LL, Damasceno BP, et al. Memory and language impairments and their relationships to hippocampal and perirhinal cortex damage in patients with medial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2006;8(3):593–600. - PubMed
-
- Arora J, Pugh K, Westerveld M, Spencer S, Spencer DD, Todd Constable R. Language lateralization in epilepsy patients: fMRI validated with the Wada procedure. Epilepsia. 2009;50(10):2225–2241. - PubMed
-
- Ashtari M. Anatomy and functional role of the inferior longitudinal fasciculus: a search that has just begun. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2012;54(1):6–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

