SWOG S0800 (NCI CDR0000636131): addition of bevacizumab to neoadjuvant nab-paclitaxel with dose-dense doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide improves pathologic complete response (pCR) rates in inflammatory or locally advanced breast cancer
- PMID: 27393622
- PMCID: PMC4963434
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-016-3889-6
SWOG S0800 (NCI CDR0000636131): addition of bevacizumab to neoadjuvant nab-paclitaxel with dose-dense doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide improves pathologic complete response (pCR) rates in inflammatory or locally advanced breast cancer
Abstract
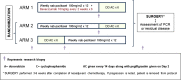
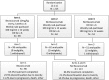
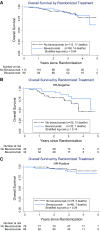
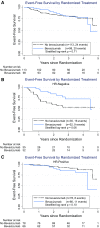
SWOG S0800, a randomized open-label Phase II clinical trial, compared the combination of weekly nab-paclitaxel and bevacizumab followed by dose-dense doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide (AC) with nab-paclitaxel followed or preceded by AC as neoadjuvant treatment for HER2-negative locally advanced breast cancer (LABC) or inflammatory breast cancer (IBC). Patients were randomly allocated (2:1:1) to three neoadjuvant chemotherapy arms: (1) nab-paclitaxel with concurrent bevacizumab followed by AC; (2) nab-paclitaxel followed by AC; or (3) AC followed by nab-paclitaxel. The primary endpoint was pathologic complete response (pCR) with stratification by disease type (non-IBC LABC vs. IBC) and hormone receptor status (positive vs. negative). Overall survival (OS), event-free survival (EFS), and toxicity were secondary endpoints. Analyses were intent-to-treat comparing bevacizumab to the combined control arms. A total of 215 patients were accrued including 11 % with IBC and 32 % with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). The addition of bevacizumab significantly increased the pCR rate overall (36 vs. 21 %; p = 0.019) and in TNBC (59 vs. 29 %; p = 0.014), but not in hormone receptor-positive disease (24 vs. 18 %; p = 0.41). Sequence of administration of nab-paclitaxel and AC did not affect the pCR rate. While no significant differences in OS or EFS were seen, a trend favored the addition of bevacizumab for EFS (p = 0.06) in TNBC. Overall, Grade 3-4 adverse events did not differ substantially by treatment arm. The addition of bevacizumab to nab-paclitaxel prior to dose-dense AC neoadjuvant chemotherapy significantly improved the pCR rate compared to chemotherapy alone in patients with triple-negative LABC/IBC and was accompanied by a trend for improved EFS. This suggests reconsideration of the role of bevacizumab in high-risk triple-negative locally advanced breast cancer.
Keywords: Bevacizumab; Breast cancer; Inflammatory; Locally advanced; Neoadjuvant.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189804/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189856/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189971/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180834/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233329/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180835/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180801/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180858/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189872/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189822/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189952/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180846/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189858/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189817/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189954/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189853/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189957/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA052654/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180888/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180819/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189953/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180830/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

