Translation of the Care of Persons with Dementia in their Environments (COPE) intervention in a publicly-funded home care context: Rationale and research design
- PMID: 27394383
- PMCID: PMC4979745
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cct.2016.07.006
Translation of the Care of Persons with Dementia in their Environments (COPE) intervention in a publicly-funded home care context: Rationale and research design
Abstract
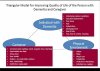
Background: Dementia is the leading cause of loss of independence in older adults worldwide. In the U.S., approximately 15 million family members provide care to relatives with dementia. This paper presents the rationale and design for a translational study in which an evidence-based, non-pharmacologic intervention for older adults with dementia and family caregivers (CGs) is incorporated into a publicly-funded home care program for older adults at risk for nursing home admission.
Methods: The 4-month Care of Persons with Dementia in their Environments (COPE) intervention is designed to optimize older adults' functional independence, and to improve CG dementia management skills and health-related outcomes. COPE features 10 in-home occupational therapy visits, and 1 in-home visit and 1 telephone contact by an advanced practice nurse. COPE was deemed efficacious in a published randomized clinical trial. In the present study, older adults with dementia enrolled in the Connecticut Home Care Program for Elders (CHCPE) and their CGs are randomly assigned to receive COPE plus their ongoing CHCPE services, or to continue receiving CHCPE services only.
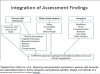
Outcomes: The primary outcome for older adults with dementia is functional independence; secondary outcomes are activity engagement, quality of life, and prevention or alleviation of neuropsychiatric symptoms. CG outcomes include perceived well-being and confidence in using activities to manage dementia symptoms. Translational outcomes include net financial benefit of COPE, and feasibility and acceptability of COPE implementation into the CHCPE. COPE has the potential to improve health-related outcomes while saving Medicaid waiver and state revenue-funded home care program costs nationwide.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02365051.
Keywords: Dementia; Family caregiving; Home care; Older adults.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Alzheimer's Disease International . World Alzheimer Report 2015: The Global Impact of Dementia: An Analysis of Prevalence, Incidence, Costs, and Trends. Alzheimer's Disease International; London: 2015.
-
- Alzheimer's Association. 2015 Alzheimer's Disease Facts and Figures. Chicago. 2015
-
- Gitlin LN, Vause Earland T. In: Improving Quality of Life in Individuals with Dementia: The Role of Nonpharmacologic Approaches in Rehabilitation. Stone B JH, editor. International encyclopedia of rehabilitation; 2009.
-
- Connecticut Home Care Program for Elders . Home Care at a Glance: SFY 2010 Annual Report to the Legislature July 2009-June 2010. Hartford; 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical