Meningeal mast cell-T cell crosstalk regulates T cell encephalitogenicity
- PMID: 27396526
- PMCID: PMC6364701
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2016.06.015
Meningeal mast cell-T cell crosstalk regulates T cell encephalitogenicity
Abstract
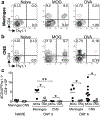
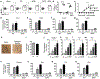
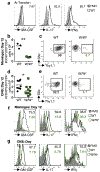
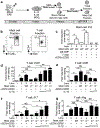
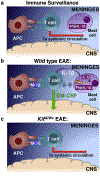
GM-CSF is a cytokine produced by T helper (Th) cells that plays an essential role in orchestrating neuroinflammation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, a rodent model of multiple sclerosis. Yet where and how Th cells acquire GM-CSF expression is unknown. In this study we identify mast cells in the meninges, tripartite tissues surrounding the brain and spinal cord, as important contributors to antigen-specific Th cell accumulation and GM-CSF expression. In the absence of mast cells, Th cells do not accumulate in the meninges nor produce GM-CSF. Mast cell-T cell co-culture experiments and selective mast cell reconstitution of the meninges of mast cell-deficient mice reveal that resident meningeal mast cells are an early source of caspase-1-dependent IL-1β that licenses Th cells to produce GM-CSF and become encephalitogenic. We also provide evidence of mast cell-T cell co-localization in the meninges and CNS of recently diagnosed acute MS patients indicating similar interactions may occur in human demyelinating disease.
Keywords: Caspase-1; Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE); GM-CSF; IL-1beta; Inflammasome; Mast cells; Meninges; Multiple sclerosis (MS); Myeloid cells; T cell licensing; T helper cells.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hauser SL, Oksenberg JR, The neurobiology of multiple sclerosis: genes, inflammation, and neurodegeneration, Neuron 52 (2006) 61–76. - PubMed
-
- Odoardi F, Sie C, Streyl K, Ulaganathan VK, Schlager C, Lodygin D, et al., T cells become licensed in the lung to enter the central nervous system, Nature 488 (2012) 675–679. - PubMed
-
- Berer K, Mues M, Koutrolos M, Rasbi ZA, Boziki M, Johner C, et al., Commensal microbiota and myelin autoantigen cooperate to trigger autoimmune demyelination, Nature 479 (2011) 538–541. - PubMed
-
- Ransohoff RM, Immunology: licensed in the lungs, Nature 488 (2012) 595–596. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

