Redox modulation of cellular stress response and lipoxin A4 expression by Hericium Erinaceus in rat brain: relevance to Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis
- PMID: 27398086
- PMCID: PMC4938991
- DOI: 10.1186/s12979-016-0078-8
Redox modulation of cellular stress response and lipoxin A4 expression by Hericium Erinaceus in rat brain: relevance to Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis
Abstract
Background: There has been a recent upsurge of interest in complementary medicine, especially dietary supplements and foods functional in delaying the onset of age-associated neurodegenerative diseases. Mushrooms have long been used in traditional medicine for thousands of years, being now increasingly recognized as antitumor, antioxidant, antiviral, antibacterial and hepatoprotective agent also capable to stimulate host immune responses.
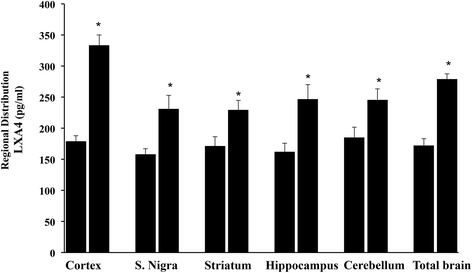
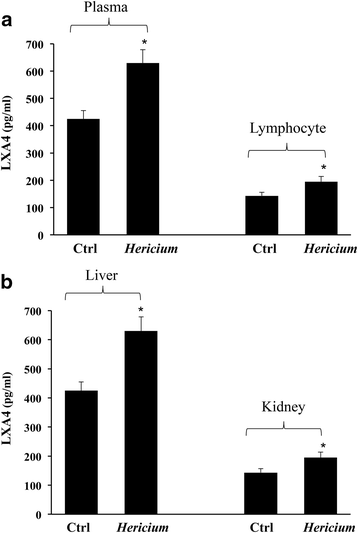
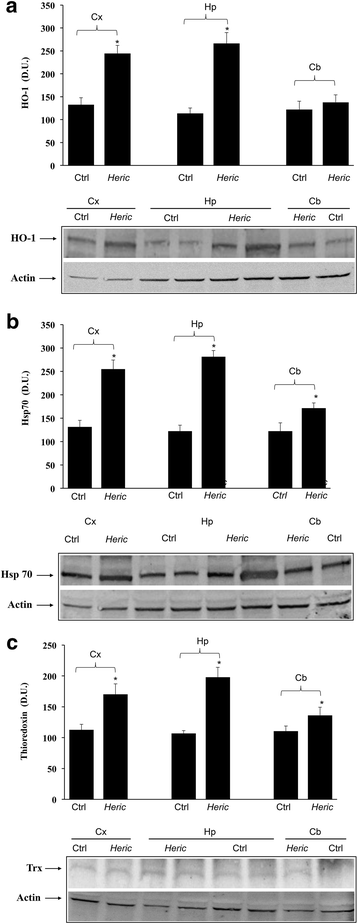
Results: Here we provide evidence of neuroprotective action of Hericium Herinaceus when administered orally to rat. Expression of Lipoxin A4 (LXA4) was measured in different brain regions after oral administration of a biomass Hericium preparation, given for 3 month. LXA4 up-regulation was associated with an increased content of redox sensitive proteins involved in cellular stress response, such as Hsp72, Heme oxygenase -1 and Thioredoxin. In the brain of rats receiving Hericium, maximum induction of LXA4 was observed in cortex, and hippocampus followed by substantia Nigra, striatum and cerebellum. Increasing evidence supports the notion that oxidative stress-driven neuroinflammation is a fundamental cause in neurodegenerative diseases. As prominent intracellular redox system involved in neuroprotection, the vitagene system is emerging as a neurohormetic potential target for novel cytoprotective interventions. Vitagenes encode for cytoprotective heat shock proteins 70, heme oxygenase-1, thioredoxin and Lipoxin A4. Emerging interest is now focussing on molecules capable of activating the vitagene system as novel therapeutic target to minimize deleterious consequences associated with free radical-induced cell damage, such as in neurodegeneration. LXA4 is an emerging endogenous eicosanoid able to promote resolution of inflammation, acting as an endogenous "braking signal" in the inflammatory process. In addition, Hsp system is emerging as key pathway for modulation to prevent neuronal dysfunction, caused by protein misfolding.
Conclusions: Conceivably, activation of LXA4 signaling and modulation of stress responsive vitagene proteins could serve as a potential therapeutic target for AD-related inflammation and neurodegenerative damage.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Heat shock protein70; Heme Oxygenase-1; Lipoxin A4; Nutritional mushrooms.
Figures



References
-
- Di Bona D, Accardi G, Virruso C, Candore G, Caruso C. Association between genetic variations in the insulin/insulin-like growth factor (Igf-1) signaling pathway and longevity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2014;12(5):674–81. doi: 10.2174/1570161111666131218152807. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

