Retroperitoneal laparoscopic partial nephrectomy for treatment of metanephric adenoma (Report of 6 cases)
- PMID: 27398273
- PMCID: PMC4936994
- DOI: 10.1186/s40064-016-2662-y
Retroperitoneal laparoscopic partial nephrectomy for treatment of metanephric adenoma (Report of 6 cases)
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the clinical and pathological features of metanephric adenoma (MA) and the clinical outcome after retroperitoneal laparoscopic nephron-sparing surgery.
Methods: Six out of 183 partial nephrectomies performed during January 2009 to August 2014 were confirmed to be MA confirmed by postoperative pathological study. Perioperative parameters of the six patients were then retrospectively collected, analyzed and compared with current literature, including warm ischemia time (WIT), total operation time, estimated blood loss (EBL), positive surgical margin (PSM), and complications. Surgical and oncological outcome of all six patients were evaluated based on a mean follow up of 17 months (5-48 months).
Results: Tumors in all six cases were all successfully removed by partial nephrectomy. Mean WIT was 24.7 min (19-35 min). Mean operation time was 103.6 min (82-147 min). Mean EBL was 53.5 ml (20-85 ml). No conversion, transfusion or other major complication were observed in all six cases. Postoperative pathology confirmed negative surgical margin in all six cases. During a mean of 17 month follow up (5-48 months), no local recurrence or metastasis were found in all six cases.
Conclusion: MA is a rare benign primary kidney epithelial cancer, which could hardly be differentiated from renal malignancies based on preoperative imaging. Our data suggested that retroperitoneal laparoscopic partial nephrectomy can be used for surgical treatment of MA, in terms of tumor control and preservation of renal function.
Keywords: Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy; Metanephric adenoma; Retroperitoneal.
Figures
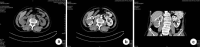


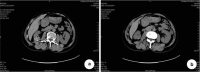
Similar articles
-
Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy for hilar tumors: technique and results.Eur Urol. 2008 Aug;54(2):409-16. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2008.04.007. Epub 2008 Apr 11. Eur Urol. 2008. PMID: 18440123
-
[A comparative analysis of laparoscopic and retroperitoneoscopic partial nephrectomy depending on the type of temporary and definite hemostasis].Urologiia. 2018 Dec;(6):95-100. Urologiia. 2018. PMID: 30742385 Russian.
-
Application and analysis of retroperitoneal laparoscopic partial nephrectomy with sequential segmental renal artery clamping for patients with multiple renal tumor: initial experience.BMC Urol. 2017 Sep 11;17(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12894-017-0272-9. BMC Urol. 2017. PMID: 28893213 Free PMC article.
-
[Retroperitoneal laparoscopic surgery and carcinogenic risk].Prog Urol. 2001 Feb;11(1):8-15. Prog Urol. 2001. PMID: 11296653 Review. French.
-
Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy.J Endourol. 2005 Jul-Aug;19(6):634-42. doi: 10.1089/end.2005.19.634. J Endourol. 2005. PMID: 16053351 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemotherapy Combined With Surgery in a Case With Metanephric Adenoma.Front Pediatr. 2022 Apr 7;10:847864. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.847864. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35463907 Free PMC article.
-
Retroperitoneal laparoscopic partial nephrectomy for metanephric adenoma in a pediatric patient - The first case report from vietnam.Urol Case Rep. 2024 Apr 10;54:102733. doi: 10.1016/j.eucr.2024.102733. eCollection 2024 May. Urol Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38655151 Free PMC article.
-
Robot-assisted versus laparoscopic partial nephrectomy for anatomically complex T1b renal tumors with a RENAL nephrometry score ≥7: A propensity score-based analysis.Cancer Med. 2020 Jan;9(2):586-594. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2749. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 31788986 Free PMC article.
-
Experience of diagnosis and management of metanephric adenoma: retrospectively analysis of 10 cases and a literature review.Transl Androl Urol. 2020 Aug;9(4):1661-1669. doi: 10.21037/tau-19-912. Transl Androl Urol. 2020. PMID: 32944527 Free PMC article.
-
Metanephric adenoma in children: A case report and literature review.Oncol Lett. 2023 Sep 27;26(5):486. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.14073. eCollection 2023 Nov. Oncol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37818137 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuroda N, Tol M, Hiroi M, Enzan H. Review of metanephric adenoma of the kidney with focus on clinical and pathobiological aspects. Histol Histopathol. 2003;18(1):253–257. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

