Anti-inflammatory Function of Phyllostachys Edulis Extract in the Hippocampus of HIV-1 Transgenic Rats
- PMID: 27398410
- PMCID: PMC4938001
- DOI: 10.16966/2380-5536.126
Anti-inflammatory Function of Phyllostachys Edulis Extract in the Hippocampus of HIV-1 Transgenic Rats
Abstract
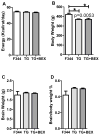
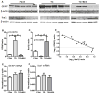
HIV induces neuroinflammation. We evaluated the anti-inflammatory effect of an extract from bamboo Phyllostachys edulis in the hippocampus of HIV-1 transgenic (TG) rats. Five (5) one-month-old TG rats and 5 Fisher 344 (F344) rats were fed a control diet, another 5 TG rats were fed the control diet supplemented with bamboo extract (BEX, 11 grams dry mass per 4057 Kcal). After 9 months of dietary treatment, the gene and protein expression of interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), and ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba1), and the protein expression p65 and c-Jun were analyzed in the hippocampus. Compared to the F344 rats, the TG rats fed control diet showed significantly higher protein expression of GFAP and c-Jun, and mRNA and protein levels of IL-1β. BEX supplement to the TG rats significantly lowered protein expressions of GFAP, p65, and c-Jun, and showed a trend to decrease the protein expression of IL-1β. Compared to the TG rats, TG+BEX rats also downregulated the mRNA levels of IL-1β and TNFα. In summary, neuroinflammation mediated by the NFκB and AP-1 pathways in the hippocampus of the TG rats was effectively abolished by dietary supplement of BEX.
Keywords: AP-1; HIV; NFκB; bamboo Phyllostachys edulis extract; hippocampus; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
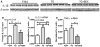
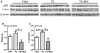
Similar articles
-
Dietary eicosapentaenoic acid normalizes hippocampal omega-3 and 6 polyunsaturated fatty acid profile, attenuates glial activation and regulates BDNF function in a rodent model of neuroinflammation induced by central interleukin-1β administration.Eur J Nutr. 2018 Aug;57(5):1781-1791. doi: 10.1007/s00394-017-1462-7. Epub 2017 May 18. Eur J Nutr. 2018. PMID: 28523372
-
Neuroprotective effect of sodium ferulate and signal transduction mechanisms in the aged rat hippocampus.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2008 Dec;29(12):1399-408. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00848.x. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2008. PMID: 19026158
-
Withania somnifera as a potential candidate to ameliorate high fat diet-induced anxiety and neuroinflammation.J Neuroinflammation. 2017 Oct 12;14(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-0975-6. J Neuroinflammation. 2017. PMID: 29025435 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of edaravone on glial fibrillary acidic protein and interleukin-lβ expression and neuronal apoptosis in juvenile rat hippocampus after status convulsion].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2011 Mar;13(3):231-5. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21426644 Chinese.
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein transcription responses to transforming growth factor-beta1 and interleukin-1beta are mediated by a nuclear factor-1-like site in the near-upstream promoter.J Neurochem. 1999 Apr;72(4):1353-61. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.721353.x. J Neurochem. 1999. PMID: 10098836
Cited by
-
Age-Related Decrease in Tyrosine Hydroxylase Immunoreactivity in the Substantia Nigra and Region-Specific Changes in Microglia Morphology in HIV-1 Tg Rats.Neurotox Res. 2019 Oct;36(3):563-582. doi: 10.1007/s12640-019-00077-z. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Neurotox Res. 2019. PMID: 31286433 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anthony IC, Ramage SN, Carnie FW, Simmonds P, Bell JE. Influence of HAART on HIV-related CNS disease and neuroinflammation. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2005;64:529–36. - PubMed
-
- Anthony IC, Bell JE. The Neuropathology of HIV/AIDS. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2008;20:15–24. - PubMed
-
- Brabers NA, Nottet HS. Role of the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha and IL-1beta in HIV-associated dementia. Eur J Clin Invest. 2006;36:447–58. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
