Predictors of chronic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes: A longitudinal study from the AMD Annals initiative
- PMID: 27399078
- PMCID: PMC5058807
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004007
Predictors of chronic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes: A longitudinal study from the AMD Annals initiative
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Predictors of chronic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes: A longitudinal study from the AMD Annals initiative: Erratum.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Dec 9;95(49):e5660. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005660. eCollection 2016 Dec. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 31265666 Free PMC article.
Abstract
The identification of clinical predictors for the development of chronic kidney disease is a critical issue in the management of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.We evaluated 27,029 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m and normoalbuminuria from the database of the Italian Association of Clinical Diabetologists network. Primary outcomes were eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m and normoalbuminuria; albuminuria and eGFR ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m; and eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m and albuminuria. Secondary outcomes were eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m and albuminuria.
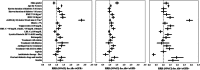
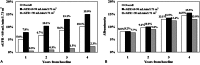
Measurements: eGFR from serum creatinine by chronic kidney disease epidemiology collaboration equation (CKD-EPI), urinary albumin excretion, HbA1c, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c), blood pressure, and body mass index.Over a 4-year period, 33.2% of patients (n = 8973) developed chronic kidney disease, 10.3% (n = 2788) showed a decline in eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m, 18.4% (n = 4978) developed albuminuria, and 4.5% (n = 1207) developed both features. Relative risk ratios (RRRs) for age (1.37, P < 0.001 by 5 years), sex (0.77, P < 0.001 for being male), body mass index (1.03, P < 0.001 by 1 kg/m), triglycerides (1.02, P < 0.001 by 10 mg/dL), and LDL-c (0.97, P = 0.004 by 10 mg/dL) were independently related to the onset of eGFR reduction. Age (1.08, P < 0.001 by 5 years), sex (1.36, P < 0.001 for being male), body mass index (1.02, P < 0.001 by 1 kg/m), triglycerides (1.01, P = 0.02 by 10 mg/dL), HDL-c, and LDL-c (0.97, P = 0.008 and 0.99, P = 0.003 by 5 and 10 mg/dL, respectively) were related to the onset of albuminuria. HbA1c and the intensity of antihypertensive treatment showed a weaker association with renal outcome.Reduction in eGFR and albuminuria showed distinct sets of risk factors, suggesting that different mechanisms are involved in the development of these 2 components of diabetic kidney disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- IDF. Diabetes Atlas. 6th ed.2013; Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation, http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlashttp://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas. Accessed July 16, 2015.
-
- Guariguata L, Whiting DR, Hambleton I, et al. Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2014; 103:137–149. - PubMed
-
- US Renal Data System. Renal Data US System USRDS 2014 Annual Data Report: Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States. Bethesda, MD: US Renal Data System; 2014.
-
- National Kidney Foundation. KDOQI clinical practice guidelines for Diabetes and CKD: 2012 update. Am J Kidney Dis 2012; 60:850–886. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

