The Arabidopsis thaliana lectin receptor kinase LecRK-I.9 is required for full resistance to Pseudomonas syringae and affects jasmonate signalling
- PMID: 27399963
- PMCID: PMC6638305
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.12457
The Arabidopsis thaliana lectin receptor kinase LecRK-I.9 is required for full resistance to Pseudomonas syringae and affects jasmonate signalling
Abstract
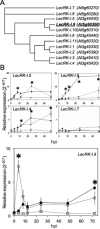
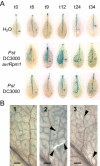
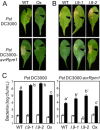
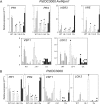
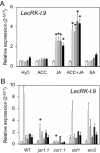
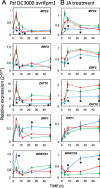
On microbial attack, plants can detect invaders and activate plant innate immunity. For the detection of pathogen molecules or cell wall damage, plants employ receptors that trigger the activation of defence responses. Cell surface proteins that belong to large families of lectin receptor kinases are candidates to function as immune receptors. Here, the function of LecRK-I.9 (At5g60300), a legume-type lectin receptor kinase involved in cell wall-plasma membrane contacts and in extracellular ATP (eATP) perception, was studied through biochemical, gene expression and reverse genetics approaches. In Arabidopsis thaliana, LecRK-I.9 expression is rapidly, highly and locally induced on inoculation with avirulent strains of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato (Pst). Two allelic lecrk-I.9 knock-out mutants showed decreased resistance to Pst. Conversely, over-expression of LecRK-I.9 led to increased resistance to Pst. The analysis of defence gene expression suggests an alteration of both the salicylic acid (SA) and jasmonic acid (JA) signalling pathways. In particular, LecRK-I.9 expression during plant-pathogen interaction was dependent on COI1 (CORONATINE INSENSITIVE 1) and JAR1 (JASMONATE RESISTANT 1) components, and JA-responsive transcription factors (TFs) showed altered levels of expression in plants over-expressing LecRK-I.9. A similar misregulation of these TFs was obtained by JA treatment. This study identified LecRK-I.9 as necessary for full resistance to Pst and demonstrated its involvement in the control of defence against pathogens through a regulation of JA signalling components. The role of LecRK-I.9 is discussed with regard to the potential molecular mechanisms linking JA signalling to cell wall damage and/or eATP perception.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; Pseudomonas; jasmonic acid; lectin; plant-pathogen interactions; receptor-like kinases.
© 2016 BSPP AND JOHN WILEY & SONS LTD.
Figures
References
-
- André, S. , Siebert, H.C. , Nishiguchi, M. , Tazaki, K. and Gabius, H.J. (2005) Evidence for lectin activity of a plant receptor‐like protein kinase by application of neoglycoproteins and bioinformatic algorithms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1725, 222–232. - PubMed
-
- Antolín‐Llovera, M. , Petutsching, E.K. , Ried, M.K. , Nürnberger, T. , Robatzek, S. and Parniske, M. (2014) Knowing your friends and foes–plant receptor‐like kinases as initiators of symbiosis and defence. New Phytol., 204, 791–802. - PubMed
-
- Armijo, G. , Salinas, P. , Monteoliva, M.I. , Seguel, A. , García, C. , Villarroel‐Candia, E. , Song, W. , van der Krol, A.R. , Álvarez, M.E. and Holuigue, L. (2013) A salicylic acid‐induced lectin‐like protein plays a positive role in the effector‐triggered immunity response of Arabidopsis thaliana to Pseudomonas syringae Avr‐Rpm1. Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact. 26, 1395–1406. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

