The mixed-lineage kinase 3 inhibitor URMC-099 facilitates microglial amyloid-β degradation
- PMID: 27401058
- PMCID: PMC4940949
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-016-0646-z
The mixed-lineage kinase 3 inhibitor URMC-099 facilitates microglial amyloid-β degradation
Abstract
Background: Amyloid-β (Aβ)-stimulated microglial inflammatory responses engage mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Mixed-lineage kinases (MLKs) regulate upstream MAPK signaling that include p38 MAPK and c-Jun amino-terminal kinase (JNK). However, whether MLK-MAPK pathways affect Aβ-mediated neuroinflammation is unknown. To this end, we investigated if URMC-099, a brain-penetrant small-molecule MLK type 3 inhibitor, can modulate Aβ trafficking and processing required for generating AD-associated microglial inflammatory responses.
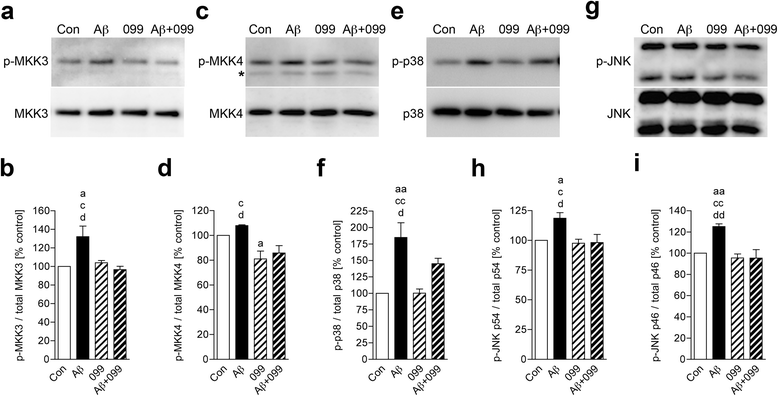
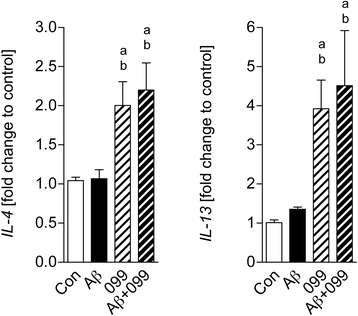
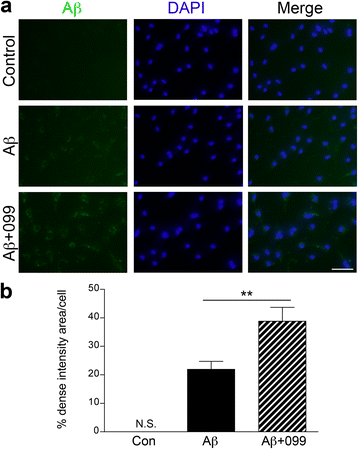
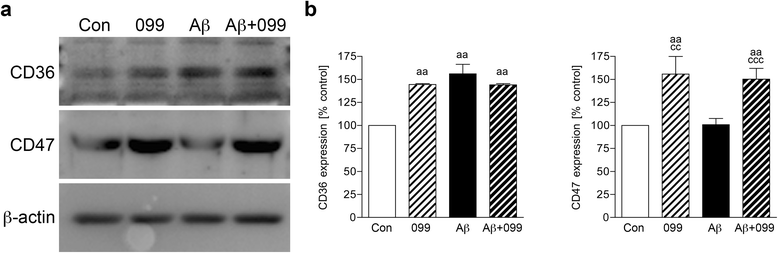
Methods: Aβ1-42 (Aβ42) and/or URMC-099-treated murine microglia were investigated for phosphorylated mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MKK)3, MKK4 (p-MKK3, p-MKK4), p38 (p-p38), and JNK (p-JNK). These pathways were studied in tandem with the expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α. Gene expression of the anti-inflammatory cytokines, IL-4 and IL-13, was evaluated by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Aβ uptake and expression of scavenger receptors were measured. Protein trafficking was assessed by measures of endolysosomal markers using confocal microscopy.
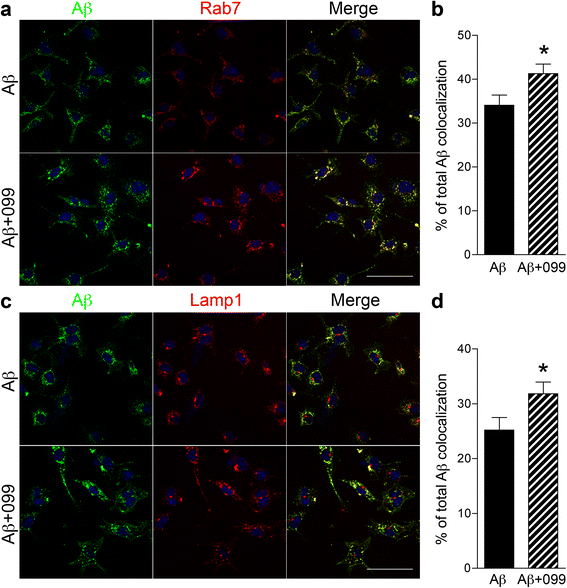
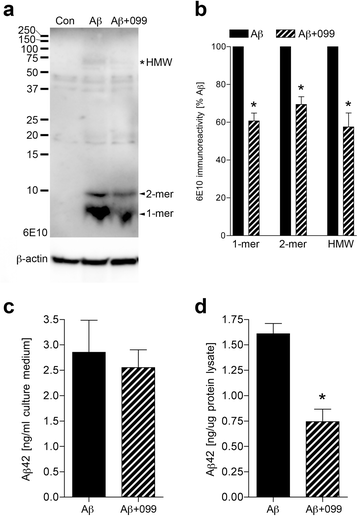
Results: Aβ42-mediated microglial activation pathways were shown by phosphorylation of MKK3, MKK4, p38, and JNK and by expression of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. URMC-099 modulated microglial inflammatory responses with induction of IL-4 and IL-13. Phagocytosis of Aβ42 was facilitated by URMC-099 with up-regulation of scavenger receptors. Co-localization of Aβ and endolysosomal markers associated with enhanced Aβ42 degradation was observed.
Conclusions: URMC-099 reduced microglial inflammatory responses and facilitated phagolysosomal trafficking with associated Aβ degradation. These data demonstrate a new immunomodulatory role for URMC-099 to inhibit MLK and to induce microglial anti-inflammatory responses. Thus, URMC-099 may be developed further as a novel disease-modifying AD therapy.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid-β; Endolysosomal pathway; Microglia; Mixed-lineage kinase 3; Phagocytosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
URMC-099 facilitates amyloid-β clearance in a murine model of Alzheimer's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 May 5;15(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1172-y. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29729668 Free PMC article.
-
LRP1 modulates the microglial immune response via regulation of JNK and NF-κB signaling pathways.J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Dec 8;13(1):304. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0772-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 27931217 Free PMC article.
-
Androgen alleviates neurotoxicity of β-amyloid peptide (Aβ) by promoting microglial clearance of Aβ and inhibiting microglial inflammatory response to Aβ.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2017 Nov;23(11):855-865. doi: 10.1111/cns.12757. Epub 2017 Sep 20. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2017. PMID: 28941188 Free PMC article.
-
Shedding light on microglial dysregulation in Alzheimer's disease: exploring molecular mechanisms and therapeutic avenues.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Feb;33(2):679-702. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01598-6. Epub 2024 Nov 28. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 39609333 Review.
-
Microglial Aβ receptors in Alzheimer's disease.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Jan;35(1):71-83. doi: 10.1007/s10571-014-0101-6. Epub 2014 Aug 23. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25149075 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mixed-lineage kinase 3 pharmacological inhibition attenuates murine nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.JCI Insight. 2017 Aug 3;2(15):e94488. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.94488. eCollection 2017 Aug 3. JCI Insight. 2017. PMID: 28768902 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy facilitates macrophage depots of sustained-release nanoformulated antiretroviral drugs.J Clin Invest. 2017 Mar 1;127(3):857-873. doi: 10.1172/JCI90025. Epub 2017 Jan 30. J Clin Invest. 2017. PMID: 28134625 Free PMC article.
-
c-JUN n-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Signaling in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease.J Cell Signal. 2022;3(1):62-78. doi: 10.33696/Signaling.3.068. J Cell Signal. 2022. PMID: 35253003 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid Amyloid Quantum Dot Nano-Bio Assemblies to Probe Neuroinflammatory Damage.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024 Sep 4;15(17):3124-3135. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.4c00183. Epub 2024 Aug 15. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39146244 Free PMC article.
-
The Mixed-Lineage Kinase Inhibitor URMC-099 Protects Hippocampal Synapses in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis.eNeuro. 2018 Dec 3;5(6):ENEURO.0245-18.2018. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0245-18.2018. eCollection 2018 Nov-Dec. eNeuro. 2018. PMID: 30627663 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

