PFA toolbox: a MATLAB tool for Metabolic Flux Analysis
- PMID: 27401090
- PMCID: PMC4940746
- DOI: 10.1186/s12918-016-0284-1
PFA toolbox: a MATLAB tool for Metabolic Flux Analysis
Abstract
Background: Metabolic Flux Analysis (MFA) is a methodology that has been successfully applied to estimate metabolic fluxes in living cells. However, traditional frameworks based on this approach have some limitations, particularly when measurements are scarce and imprecise. This is very common in industrial environments. The PFA Toolbox can be used to face those scenarios.
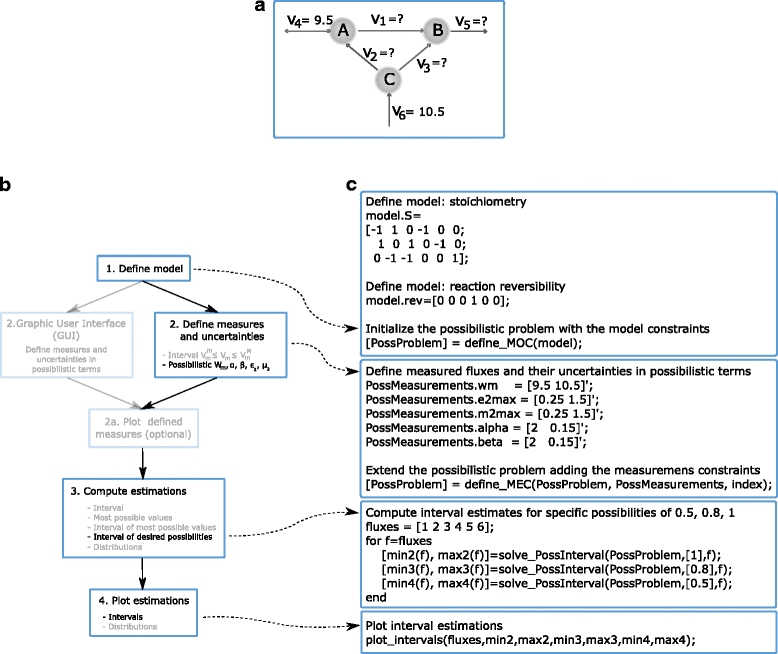
Results: Here we present the PFA (Possibilistic Flux Analysis) Toolbox for MATLAB, which simplifies the use of Interval and Possibilistic Metabolic Flux Analysis. The main features of the PFA Toolbox are the following: (a) It provides reliable MFA estimations in scenarios where only a few fluxes can be measured or those available are imprecise. (b) It provides tools to easily plot the results as interval estimates or flux distributions. (c) It is composed of simple functions that MATLAB users can apply in flexible ways. (d) It includes a Graphical User Interface (GUI), which provides a visual representation of the measurements and their uncertainty. (e) It can use stoichiometric models in COBRA format. In addition, the PFA Toolbox includes a User's Guide with a thorough description of its functions and several examples.
Conclusions: The PFA Toolbox for MATLAB is a freely available Toolbox that is able to perform Interval and Possibilistic MFA estimations.
Keywords: Constraint-based modelling; Interval MFA; Metabolic Flux Analysis; Possibilistic MFA.
Figures


References
-
- Wittmann C. Tools and Applications of Biochemical Engineering Science. Berlin: Springer; 2002. Metabolic flux analysis using mass spectrometry; pp. 39–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

