Posttranscriptional regulation of 14-3-3ζ by RNA-binding protein HuR modulating intestinal epithelial restitution after wounding
- PMID: 27401462
- PMCID: PMC4945840
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.12858
Posttranscriptional regulation of 14-3-3ζ by RNA-binding protein HuR modulating intestinal epithelial restitution after wounding
Abstract
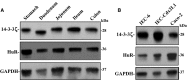
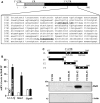
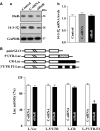
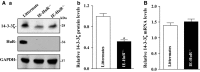
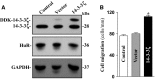
The 14-3-3ζ is a member of the family of 14-3-3 proteins and participates in many aspects of cellular processes, but its regulation and involvement in gut mucosal homeostasis remain unknown. Here, we report that 14-3-3ζ expression is tightly regulated at the posttranscription level by RNA-binding protein HuR and plays an important role in early intestinal epithelial restitution after wounding. The 14-3-3ζ was highly expressed in the mucosa of gastrointestinal tract and in cultured intestinal epithelial cells (IECs). The 3' untranslated region (UTR) of the 14-3-3ζ mRNA was bound to HuR, and this association enhanced 14-3-3ζ translation without effect on its mRNA content. Conditional target deletion of HuR in IECs decreased the level of 14-3-3ζ protein in the intestinal mucosa. Silencing 14-3-3ζ by transfection with specific siRNA targeting the 14-3-3ζ mRNA suppressed intestinal epithelial restitution as indicated by a decrease in IEC migration after wounding, whereas ectopic overexpression of the wild-type 14-3-3ζ promoted cell migration. These results indicate that HuR induces 14-3-3ζ translation via interaction with its 3' UTR and that 14-3-3ζ is necessary for stimulation of IEC migration after wounding.
Keywords: Epithelial cell migration; mucosal injury; posttranscriptional regulation; rapid epithelial repair.
© 2016 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American Physiological Society and The Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The RNA-binding protein HuR regulates intestinal epithelial restitution by modulating Caveolin-1 gene expression.Biochem J. 2021 Jan 15;478(1):247-260. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20200372. Biochem J. 2021. PMID: 33346337
-
RNA-binding protein HuR regulates translation of vitamin D receptor modulating rapid epithelial restitution after wounding.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 Jul 1;319(1):C208-C217. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00009.2020. Epub 2020 May 20. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32432928 Free PMC article.
-
HuR Enhances Early Restitution of the Intestinal Epithelium by Increasing Cdc42 Translation.Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Mar 17;37(7):e00574-16. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00574-16. Print 2017 Apr 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28031329 Free PMC article.
-
Properties of the Regulatory RNA-Binding Protein HuR and its Role in Controlling miRNA Repression.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;700:106-23. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-7823-3_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21755477 Review.
-
Posttranslational control of HuR function.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2017 Jan;8(1):10.1002/wrna.1372. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1372. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2017. PMID: 27307117 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Neutrophil Proteomic Signature in Surgical Trauma Wounds.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 7;19(3):761. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030761. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29518953 Free PMC article.
-
c-Jun enhances intestinal epithelial restitution after wounding by increasing phospholipase C-γ1 transcription.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017 Apr 1;312(4):C367-C375. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00330.2016. Epub 2017 Jan 18. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28100486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bialkowska, K. , Zaffran Y., Meyer S. C., and Fox J. E.. 2003. 14‐3‐3 ζ mediates integrin‐induced activation of Cdc42 and Rac. Platelet glycoprotein Ib‐IX regulates integrin‐induced signaling by sequestering 14‐3‐3 ζ. J. Biol. Chem. 278:33342–33350. - PubMed
-
- Chen, M. , Liu T., Xu L., Gao X., Liu X., Wang C., et al. 2014. Direct interaction of 14‐3‐3ζ with ezrin promotes cell migration by regulating the formation of membrane ruffle. J. Mol. Biol. 426:3118–3133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

