The Nrd1-like protein Seb1 coordinates cotranscriptional 3' end processing and polyadenylation site selection
- PMID: 27401558
- PMCID: PMC4949328
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.280222.116
The Nrd1-like protein Seb1 coordinates cotranscriptional 3' end processing and polyadenylation site selection
Abstract
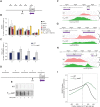
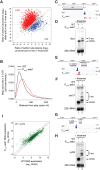
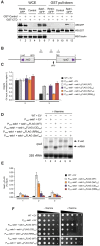
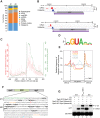
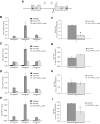
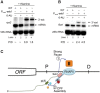
Termination of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) transcription is associated with RNA 3' end formation. For coding genes, termination is initiated by the cleavage/polyadenylation machinery. In contrast, a majority of noncoding transcription events in Saccharomyces cerevisiae does not rely on RNA cleavage for termination but instead terminates via a pathway that requires the Nrd1-Nab3-Sen1 (NNS) complex. Here we show that the Schizosaccharomyces pombe ortholog of Nrd1, Seb1, does not function in NNS-like termination but promotes polyadenylation site selection of coding and noncoding genes. We found that Seb1 associates with 3' end processing factors, is enriched at the 3' end of genes, and binds RNA motifs downstream from cleavage sites. Importantly, a deficiency in Seb1 resulted in widespread changes in 3' untranslated region (UTR) length as a consequence of increased alternative polyadenylation. Given that Seb1 levels affected the recruitment of conserved 3' end processing factors, our findings indicate that the conserved RNA-binding protein Seb1 cotranscriptionally controls alternative polyadenylation.
Keywords: 3′ end processing; Nrd1; S. pombe; Seb1; polyadenylation; transcription termination.
© 2016 Lemay et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

References
-
- Ahn SH, Kim M, Buratowski S. 2004. Phosphorylation of serine 2 within the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain couples transcription and 3′ end processing. Mol Cell 13: 67–76. - PubMed
-
- Arigo JT, Eyler DE, Carroll KL, Corden JL. 2006. Termination of cryptic unstable transcripts is directed by yeast RNA-binding proteins Nrd1 and Nab3. Mol Cell 23: 841–851. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
