Effects of the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device on the immune microenvironment of the human cervix and endometrium
- PMID: 27401588
- PMCID: PMC5316474
- DOI: 10.1111/aji.12535
Effects of the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device on the immune microenvironment of the human cervix and endometrium
Abstract
Problem: There is little information regarding the impact of the intrauterine device on immune parameters of the upper female reproductive tract related to risk of HIV acquisition.
Method of study: We collected cervical and endometrial samples from women using the hormonal intrauterine device to study its effects on endocervical cytokines/chemokine concentrations, phenotypic markers of T cells, responses of endometrial T cells to activation, and alterations of endometrial cellular infiltrates.
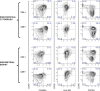
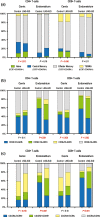
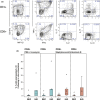
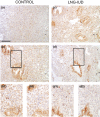
Results: Hormonal intrauterine device use was associated with: increased concentrations of inflammatory cytokines/chemokines (endocervix); increased coexpression of CXCR4 and CCR5 (endocervix and endometrium); increased coexpression of CD38 and HLADR (endocervix and endometrium); increased intracellular IL-10 production after T-cell stimulation (endometrium); and increased density of T cells, most notably regulatory T cells (endometrium).
Conclusion: Hormonal intrauterine device use resulted in both inflammatory and immunosuppressive alterations. Further research is needed to determine the significance of these changes for HIV risk.
Keywords: HIV; IUD; T-cell; chemokine; cytokine; progestin.
© 2016 The Authors. American Journal of Reproductive Immunology Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- UNAIDS . The Gap Report. Geneva: Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS; 2014.
-
- Buhling KJ, Zite NB, Lotke P, Black K, Group IW . Worldwide use of intrauterine contraception: a review. Contraception. 2014;89:162–173. - PubMed
-
- United Nations . World Contraceptive Patterns 2013. http://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/publications/family/con.... Accessed March 12, 2016.
-
- Blumenthal PD, Voedisch A, Gemzell‐Danielsson K. Strategies to prevent unintended pregnancy: increasing use of long‐acting reversible contraception. Hum Reprod Update. 2011;17:121–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

