Elasticity mapping of murine abdominal organs in vivo using harmonic motion imaging (HMI)
- PMID: 27401609
- PMCID: PMC5048218
- DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/61/15/5741
Elasticity mapping of murine abdominal organs in vivo using harmonic motion imaging (HMI)
Abstract
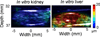
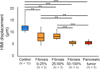
Recently, ultrasonic imaging of soft tissue mechanics has been increasingly studied to image otherwise undetectable pathologies. However, many underlying mechanisms of tissue stiffening remain unknown, requiring small animal studies and adapted elasticity mapping techniques. Harmonic motion imaging (HMI) assesses tissue viscoelasticity by inducing localized oscillation from a periodic acoustic radiation force. The objective of this study was to evaluate the feasibility of HMI for in vivo elasticity mapping of abdominal organs in small animals. Pathological cases, i.e. chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer, were also studied in vivo to assess the capability of HMI for detection of the change in mechanical properties. A 4.5 MHz focused ultrasound transducer (FUS) generated an amplitude-modulated beam resulting in 50 Hz harmonic tissue oscillations at its focus. Axial tissue displacement was estimated using 1D-cross-correlation of RF signals acquired with a 7.8 MHz diagnostic transducer confocally aligned with the FUS. In vitro results in canine liver and kidney showed the correlation between HMI displacement and Young's moduli measured by rheometry compression testing. HMI was capable of providing reproducible elasticity maps of the mouse abdominal region in vivo allowing the identification of, from stiffest to softest, the murine kidney, pancreas, liver, and spleen. Finally, pancreata affected by pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer showed HMI displacements 1.7 and 2.2 times lower than in the control case, respectively, indicating higher stiffness. The HMI displacement amplitude was correlated with the extent of fibrosis as well as detecting the very onset of stiffening even before fibrosis could be detected on H&E. This work shows that HMI can produce reliable elasticity maps of mouse abdominal region in vivo, thus providing a potentially critical tool to assess pathologies affecting organ elasticity.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Feasibility of Harmonic Motion Imaging Using a Single Transducer: In Vivo Imaging of Breast Cancer in a Mouse Model and Human Subjects.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2021 May;40(5):1390-1404. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2021.3055779. Epub 2021 Apr 30. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33523806 Free PMC article.
-
Non-contact, ultrasound-based indentation method for measuring elastic properties of biological tissues using harmonic motion imaging (HMI).Phys Med Biol. 2015 Apr 7;60(7):2853-68. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/60/7/2853. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Phys Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 25776065 Free PMC article.
-
Simulation study of amplitude-modulated (AM) harmonic motion imaging (HMI) for stiffness contrast quantification with experimental validation.Ultrason Imaging. 2010 Jul;32(3):154-76. doi: 10.1177/016173461003200304. Ultrason Imaging. 2010. PMID: 20718245
-
Acoustic radiation force elasticity imaging in diagnostic ultrasound.IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2013 Apr;60(4):685-701. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2013.2617. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2013. PMID: 23549529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Theoretical Approach in Applying High-Frequency Acoustic and Elasticity Microscopy to Assess Cells and Tissues.Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2025 May;27(1):283-305. doi: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-112823-103134. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2025. PMID: 39971347 Review.
Cited by
-
Acoustic Radiation Force Based Ultrasound Elasticity Imaging for Biomedical Applications.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Jul 12;18(7):2252. doi: 10.3390/s18072252. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30002352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experimental pancreatic cancer develops in soft pancreas: novel leads for an individualized diagnosis by ultrafast elasticity imaging.Theranostics. 2019 Aug 14;9(22):6369-6379. doi: 10.7150/thno.34066. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31588223 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of Harmonic Motion Imaging Using a Single Transducer: In Vivo Imaging of Breast Cancer in a Mouse Model and Human Subjects.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2021 May;40(5):1390-1404. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2021.3055779. Epub 2021 Apr 30. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33523806 Free PMC article.
-
An Efficient and Multi-Focal Focused Ultrasound Technique for Harmonic Motion Imaging.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2023 Apr;70(4):1150-1161. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2022.3211465. Epub 2023 Mar 21. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2023. PMID: 36191094 Free PMC article.
-
Fast lesion mapping during HIFU treatment using harmonic motion imaging guided focused ultrasound (HMIgFUS) in vitro and in vivo.Phys Med Biol. 2017 Apr 21;62(8):3111-3123. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/aa6024. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Phys Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28323638 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arda K, Ciledag N, Aktas E, Aribas BK, Köse K. Quantitative assessment of normal soft-tissue elasticity using shear-wave ultrasound elastography. Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197:532–536. - PubMed
-
- Ardito CM, Grüner BM, Takeuchi KK, Lubeseder-Martellato C, Teichmann N, Mazur PK, DelGiorno KE, Carpenter ES, Halbrook CJ, Hall JC, Pal D, Briel T, Herner A, Trajkovic-Arsic M, Sipos B, Liou GY, Storz P, Murray NR, Threadgill DW, Sibilia M, Washington MK, Wilson CL, Schmid RM, Raines EW, Crawford HC, Siveke JT. EGF Receptor Is Required for KRAS-Induced Pancreatic Tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 2012;22:304–317. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barry CT, Hah Z, Partin A, Mooney RA, Chuang KH, Augustine A, Almudevar A, Cao W, Rubens DJ, Parker KJ. Mouse liver dispersion for the diagnosis of early-stage fatty liver disease: A 70-sample study. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2014;40:704–713. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
