Designing and delivering facilitated storytelling interventions for chronic disease self-management: a scoping review
- PMID: 27401836
- PMCID: PMC4940988
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-016-1474-7
Designing and delivering facilitated storytelling interventions for chronic disease self-management: a scoping review
Abstract
Background: Little is known about how to develop and deliver storytelling as an intervention to support those managing chronic illnesses. This scoping review aims to describe the core elements of storytelling interventions in order to help facilitate its implementation.
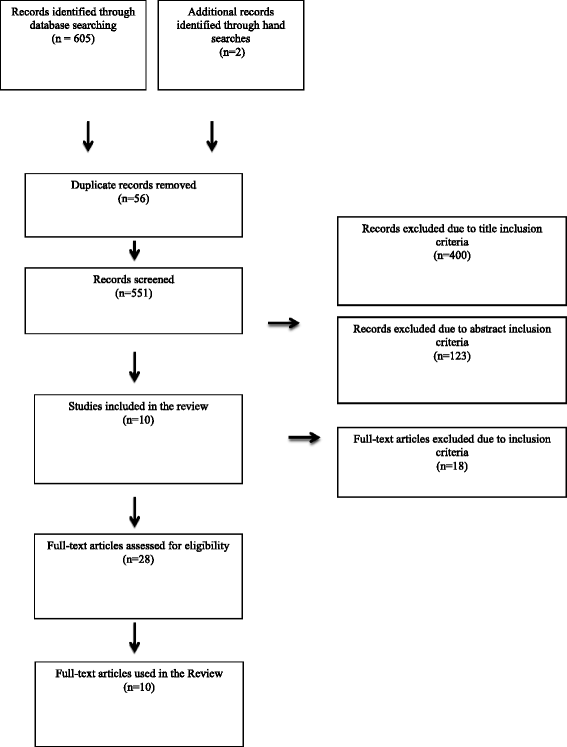
Methods: A scoping review was conducted in seven databases for articles published up to May 2014 to identify interventions that describe in detail how storytelling was used to support people in disease self-management interventions.
Results: Ten articles met all inclusion criteria. Core elements consistently observed across the storytelling interventions were: reflection and interactive meaning-making of experiences; principles of informality and spontaneity; non-directional and non-hierarchical facilitation; development of group norms and conduct to create a community among participants; and both an individual and collective role for participants. Differences were also observed across interventions, such as: the conceptual frameworks that directed the design of the intervention; the type and training of facilitators; intervention duration; and how session topics were selected and stories delivered. Furthermore, evaluation of the intervention and outcome assessment varied greatly across studies.
Conclusion: The use of storytelling can be a novel intervention to enhance chronic disease self-management. The core elements identified in the review inform the development of the intervention to be more patient-centred by guiding participants to take ownership of and lead the intervention, which differs significantly from traditional support groups. Storytelling has the potential to provide patients with a more active role in their health care by identifying their specific needs as well as gaps in knowledge and skills, while allowing them to form strong bonds with peers who share similar disease-related experiences. However, measures of impact differed across interventions given the variation in chronic conditions. Our findings can guide future development and implementations of storytelling interventions.
Keywords: Chronic disease; Chronic illness; Group education; Health education; Narration; Narrative; Patient education; Patient self-management; Peer support; Self-care; Self-management; Storytelling.
Figures
References
-
- Stuckey HL. Healing from dry bones: creative expression and adult learning in diabetes care. a thesis in adult education. The Pennsylvania State University. The graduate school. College of education. 2007
-
- Gucciardi E, Demelo M, Offenheim A, Grace SL, Stewart DE. Patient factors associated with attrition from a self-management education programme 6. J Eval Clin Pract. 2007;13:913–9. - PubMed
-
- Gucciardi E, Horodezny S, Swartzack S, Khan S, Chan VWS, Fortugno M. Primary care physician referral patterns to diabetes education programs in Southern Ontario, Canada. Can J Diab. 2012;35:262–8. doi: 10.1016/S1499-2671(11)53009-6. - DOI
-
- Gucciardi E, Chan VWS, Chuen BK, Fortugno M, Horodezny S, Swartzack S. Patient Factors and Perceived Barriers in Attending Diabetes Education Programs. 780. Can J Diab. 2012;36:214–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2012.07.009. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous