Role of Adiposity-Driven Inflammation in Depressive Morbidity
- PMID: 27402495
- PMCID: PMC5143483
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2016.123
Role of Adiposity-Driven Inflammation in Depressive Morbidity
Abstract
Depression and metabolic disorders, including overweight and obesity, appear tightly interrelated. The prevalence of these conditions is concurrently growing worldwide, and both depression and overweight/obesity represent substantial risk factors for multiple medical complications. Moreover, there is now multiple evidence for a bidirectional relationship between depression and increased adiposity, with overweight/obesity being associated with an increased prevalence of depression, and in turn, depression augmenting the risk of weight gain and obesity. Although the reasons for this intricate link between depression and increased adiposity remain unclear, converging clinical and preclinical evidence points to a critical role for inflammatory processes and related alterations of brain functions. In support of this notion, increased adiposity leads to a chronic low-grade activation of inflammatory processes, which have been shown elsewhere to have a potent role in the pathophysiology of depression. It is therefore highly possible that adiposity-driven inflammation contributes to the development of depressive disorders and their growing prevalence worldwide. This review will present recent evidence in support of this hypothesis and will discuss the underlying mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Altogether, findings presented here should help to better understand the mechanisms linking adiposity to depression and facilitate the identification of new preventive and/or therapeutic strategies.
Figures

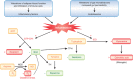

References
-
- Alciati A, D'Ambrosio A, Foschi D, Corsi F, Mellado C, Angst J (2007). Bipolar spectrum disorders in severely obese patients seeking surgical treatment. J Affect Disord 101: 131–138. - PubMed
-
- Andre C, Dinel AL, Ferreira G, Laye S, Castanon N (2014). Diet-induced obesity progressively alters cognition, anxiety-like behavior and lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior: focus on brain indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activation. Brain Behav Immun 41: 10–21. - PubMed
-
- Andre C, O'Connor JC, Kelley KW, Lestage J, Dantzer R, Castanon N (2008). Spatio-temporal differences in the profile of murine brain expression of proinflammatory cytokines and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in response to peripheral lipopolysaccharide administration. J Neuroimmunol 200: 90–99. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

